-
Biosensing by a Terahertz Chemical Microscopy
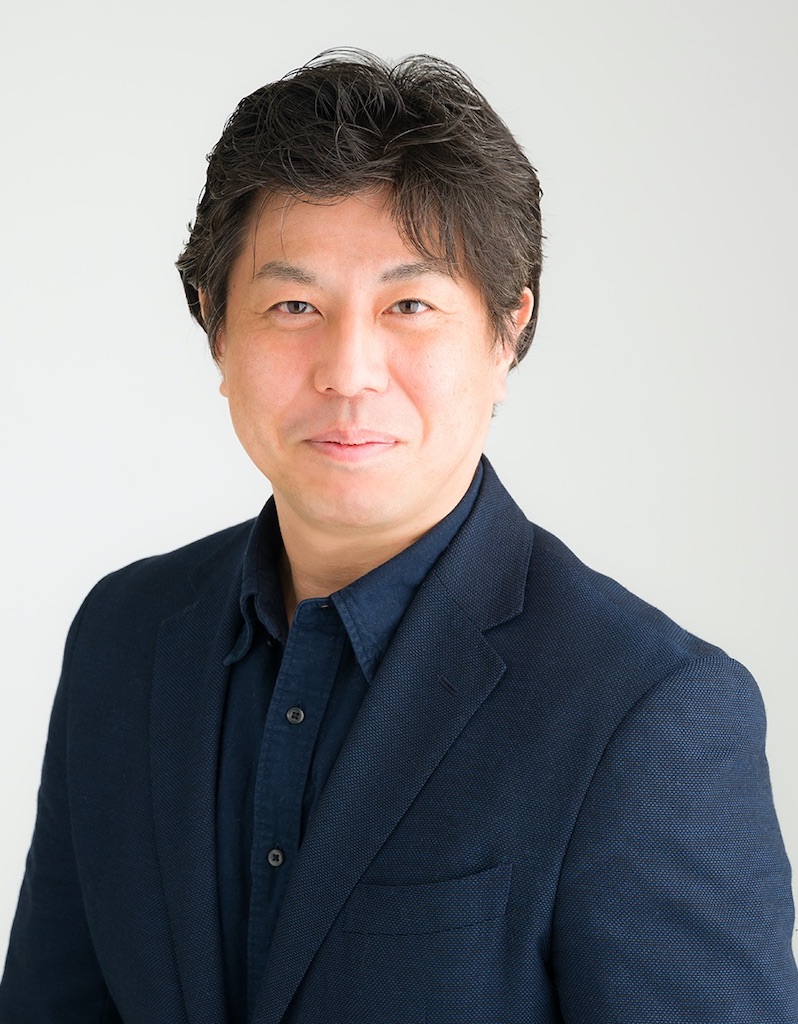
紀和利彦, DING Xue, 村上真菜, 劉長江, 井上博文, WANG Jin
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2025
2025
-
Development of platinum ultra-thin film hydrogen sensors operating at room temperatures
紀和利彦, 王裕基, 中山榛人, 王しん, 塚田啓二
検査技術
29
(
11
)
1
-
6
2024.11
-
Defect Evaluation in Mild Steel Plate Using Harmonic Ratio Induced by Square Wave Excitation Field and Nonlinear Magnetization
Moh Mawardi Saari, Mohd Aufa Hadi Putera Zaini, Mohd Herwan Sulaiman, Ahmad Salihin Samsudin, Toshihiko Kiwa
2024 IEEE International Magnetic Conference - Short papers (INTERMAG Short papers)
1
-
2
2024.5
-
Report: International Symposium organized by Graduate school of interdisciplinary science and engineering in health systems
4
27
-
29
2024.3
-
Terahertz Chemical Sensing of Cortisol Through Comparative Analysis of Antibody and Aptamer Recognition: 抗体とアプタマー認識の比較分析によるコルチゾールのテラヘルツ化学センシング: ケミカルセンサ研究会 香りの計測と心理・生理学的効果の応用およびケミカルセンサ一般
2024
(
1-4
)
1
-
3
2024.3
-
Development of compact measurement system evaluating frequency properties of magnetic nanoparticles and its application to magnetic immune assay.
伊永陸哉, 山下慶, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
2024
2024
-
Development of Voltage-Controlled Terahertz Chemical Microscope for The High-Sensitive Detection of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells
村上真菜, DING Xue, 辻紗也佳, WANG Jin, 井上博文, 紀和利彦
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
71st
2024
-
Development of Large-Bore Magnetic Particle Imaging System for Human brain imaging
野村航大, 鷲野将臣, 松田哲也, 清野智史, 中川貴, 紀和利彦
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
48th
2024
-
English lectures for introducing Okayama university to international students
3
73
-
74
2023.3
-
生体向け高感度磁気粒子イメージング装置の開発—Development of magnetic particle imaging device for biomedical applications—磁性材料を活用したバイオ・医療応用
野村 航大, 鷲野 将臣, 松田 哲也, 清野 智史, 中川 貴, 紀和 利彦
社団法人日本磁気学会研究会資料 = Bulletin of Topical Symposium of the Magnetics Society of Japan
241
1
-
5
2023.3
-
Development of SARS-CoV-2 detection technology by aptamers using a terahertz chemical microscope
辻紗也佳, DING Xue, 村上真菜, 井上博文, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
70th
2023
-
Optical Properties of silver fractal nano particles using a time-domein terahertz spectroscopy
田中宏弥, 武安伸幸, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
2023
2023
-
Self-growth of silver tree-like fractal structures and their surface-enhanced Raman application
武安伸幸, 狩野旬, 大久保貴広, 紀和利彦, MA Qingyuan, 庄司暁
フォトニクスニュース(Web)
9
(
2
)
83
-
87
2023
-
神経伝達物質を検知するテラヘルツ波バイオセンサーの開発
森田滉生, 吉田聡太, 光田祐太, 逢坂大樹, 笠原真悟, 王しん, 紀和利彦
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
40th
2023
-
Development of Flexible Ultra-Thin Film Hydrogen Sensor
王裕基, 若林翔貴, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
40th
2023
-
Silver tree-like structures self-grown under light illumination
菱井有莉, 並木潮美, 大久保貴広, 狩野旬, 紀和利彦, 庄司暁, 武安伸幸
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
70th
2023
-
Simultaneous Detection of Hydrogen gas using Ultra-Thin Platinum Film Hydrogen Sensor with Twin-T Type Notch Filter
若林翔貴, 王裕基, 中山榛人, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
74th
2023
-
Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells Detection by Voltage-Applied Terahertz Chemical Microscope
村上真菜, 辻紗也佳, DING Xue, WANG Jin, 井上博文, 紀和利彦
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
74th
2023
-
Stable Magnetic Field Application Method for Detection of Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Magnetic Sensors
岩佐祥平, 西村蓮, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 堺健司
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
74th
2023
-
DEVELOPMENT OF THICKNESS MEASUREMENT FOR STEEL SHEET PILES WITHOUT REMOVAL OF ADHERED PRODUCTS
ISHIKAWA Toshiyuki, TSUKADA Keiji, SAKAI Kenji, KIWA Toshihiko, HORI Kengo, FUKUDA Hidenori
Infrastructure Maintenance Practices
2
(
1
)
118
-
125
2023
-
Sensitivity Improvement of TCM by Voltage Modulation of Depletion Layer
村上真菜, 辻紗也佳, DING Xue, WANG Jin, 井上博文, 紀和利彦
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
2023
2023
-
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering with silica-coated silver tree-like structure
渡部紘也, 菱井有莉, 紀和利彦, 庄司暁, 大久保貴広, 狩野旬, 武安伸幸
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
70th
2023
-
Selective Detection of Calcium Ions Using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
吉田聡太, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, WANG Jin
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
70th
2023
-
Thickness Evaluation of Thermal Spray Coating on Thermally Affected Steel Pipe Using Eddy Current Testing
岡崎康佑, 山川智揮, 木下育, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 堺健司
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
26th
2023
-
Evaluation of Magnetic Response from Metal Laminated Structure for Detection of Li-ion Batteries in Small Home Appliances
岩佐祥平, 青木良太, 滝山恭生, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 堺健司
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
26th
2023
-
Development of magnetic particle imaging device for biomedical applications
野村航大, 鷲野将臣, 松田哲也, 清野智史, 中川貴, 紀和利彦
日本磁気学会研究会資料
241st
2023
-
Development of magnetic nanoparticle dispersion method using femtosecond laser
朝山柊, 加古朔也, 山本泰起, 山下慶, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
47th
2023
-
Quantitative evaluation of viscous effects on the relaxation time of magnetic nanoparticles
鷲野将臣, 野村航大, 松田哲也, 清野智史, 中川貴, 紀和利彦, 田中晶子, 坂根稔康
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
47th
2023
-
Viscosity measurement of biological solvents using HTS-SQUID with magnetic nanoparticles
山下慶, 朝山柊, 守屋列神, 山本泰起, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告(Web)
123
(
153(SCE2023 1-11)
)
2023
-
Estimation of Weld Cracks in T-Shaped Structures Using 6ch Probe for Magnetic Flux Leakage Testing
安藤雄人, 足立祥哉, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
26th
2023
-
Development of in vitro magnetic particle imaging method using relaxation time difference
野村航大, 鷲野将臣, 松田哲也, 清野智史, 中川貴, 紀和利彦
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
47th
2023
-
Development of Ultra-Thin Platinum Hydrogen Sensors with a Twin-T Filter Circuit
若林翔貴, 森貴啓, WANG Jin, 堺健二, 紀和利彦
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
39
3p
2022.11
-
Evaluation of magnetic properties of magnetic nanoparticles in buffer solution for Magnetic Particle Imaging
Nomura K., Yamauchi K., Washino M., Matsuda T., Okada Y., Susumu Y., Seino S., Nakagawa T., Kiwa T., Tonooka S.
Transaction of the Magnetics Society of Japan Special Issues
6
(
2
)
116
-
120
2022.9
-
Highly Sensitive Hydrogen Sensors for Hydrogen-energy-based Society
紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
化学工業
73
(
9
)
576
-
581
2022.9
-
Detection of Cortisol Using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
Ando Masaki, Wang Jin, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2022.1
852
-
852
2022.2
-
Detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene Using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
Nagata Hiroki, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Wang Jin
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2022.1
853
-
853
2022.2
-
Evaluation of Magnetic Properties of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Blood Using HTS-SQUID Magnetic Immunoassay System
Yamashita Kei, Tsubota Misaki, Kishimoto Kouhei, Kuroda Hiroto, Wang Jin, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2022.1
1827
-
1827
2022.2
-
Development of Lung Cancer Cell Detection Technology in Liquid Phase Using a Terahertz Chemical Microscope
DING XUE, Tsuji Sayaka, Yoshida Yuichi, Iwatsuki Kohei, Inoue Hirofumi, Wang Jin, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2022.1
858
-
858
2022.2
-
全固体電池の測定に向けたテラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡の開発
山口武人, 冨江涼太, 浜田果周, 樋口拓実, 寺西貴志, 王しん, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
シンポジウムテラヘルツ科学の最先端(CD-ROM)
9th
2022
-
Optimization of magnetic measurement method for corrosion inspection of iron-steel structures located in water
足立祥哉, 川上太聖, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 石川敏之, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
25th
2022
-
Development of nondestructive thickness measurement method for thermal spray coating under thermal effect using eddy current testing
山川智揮, 岡崎康佑, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 堺健司
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
25th
2022
-
Development of 6 ch Probe Based on Magnetic Flux Leakage Method and Visualization of Crakes in Welding Part
安藤雄人, 足立祥哉, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
73rd
2022
-
Terahertz Chemical Microscope Imaging System for 2, 4, 6-Trinitrotoluene Detection
WANG Jin, 紀和利彦
Annual Report of the Okayama Foundation for Science and Technology
(
31
)
2022
-
Application of a terahertz chemical microscope
紀和利彦, 葭田勇一, DING Xue, 辻紗也佳, 岩附康平, 谷泉克弥, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 井上博文
日本化学会春季年会講演予稿集(Web)
102nd
2022
-
Detection of internal cracks in steel materials using dual-frequency magnetic signal
安藤雄人, 足立祥哉, 川上太聖, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 石川敏之, 廣畑幹人
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2022
2022
-
Development of All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Battery Potential Distribution Measurement System Using Terahertz Waves
冨江涼太, 山口武人, 浜田果周, 寺西貴志, 能勢秀俊, 小林正樹, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
2022
2022
-
Improvement in Sensitivity of Frequency Characteristic Evaluation System for Magnetic Nanoparticles
守屋列神, 山本泰起, 黒田滉人, 岸本航平, 山下慶, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
73rd
2022
-
Evaluation of Magnetic Response from Li-ion Batteries and Various Metals for Detection of Batteries Inside Small Home Appliances Using Magnetic Sensors
岩佐祥平, 青木良太, 滝山恭生, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 堺健司
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
73rd
2022
-
Development of highly sensitive evaluation system for AC magnetization characteristics of magnetic nanoparticles using HTS-SQUID
黒田滉人, 守屋列神, 山本泰起, 岸本航平, 山下慶, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
104th
2022
-
Detection of cancer cells using immune reaction with a terahertz chemical microscope
Jin Wang, K. Iwatsuki, Kenji Sakai, Yuichi Yoshida, Toshihiko Kiwa, Xue Ding, Hirofumi Inoue
2021 46th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz)
1
-
2
2021.8
-
Evaluation of Cosmetic Liquid Penetration Using Terahertz Time-of-Flight Method
Toshihiko Kiwa, Tomoya Niki, Tomoki Kotani, Kenji Sakai, Jin Wang
2021 46th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz)
1
-
2
2021.8
-
Development of dispersion method of magnetic nanoparticles by femtosecond laser for magnetic immune assay using HTS-SQUID
Kishimoto Kouhei, Kuroda Hiroto, Tsubota Misaki, Yamashita Kei, Wang Jin, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2021.2
2039
-
2039
2021.8
-
Development of Impedance Measurement of Lithium Ion Batteries Electrode using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
清水雅司, 山中亮治, 寺西貴志, Wang Jin, 堺健司, 塚田啓二, 紀和利彦
電気学会論文誌 E
141
(
8
)
2021
-
Sub-picosecond-scale electro potential measurement of photocatalysts
紀和利彦, 堺健司
Annual Report of the Okayama Foundation for Science and Technology
(
30
)
2021
-
Evaluation of Environmental Magnetic Noise Generated by Automobiles
齊藤大介, 小嵐愛子, 林実, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会論文特集号(Web)
5
(
1
)
2021
-
Change in magnetic properties of water by electrolytes
山下慶, 坪田美咲, 平松文太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2021
2021
-
Study on the Shape of Sensitive part of Bridge Type Ultra-thin Film Hydrogen Sensor
森貴啓, 小部寛斗, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 塚田啓二, 紀和利彦, 近藤健二, 高橋琢哉, 中川眞, 上田尚宏
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2021
2021
-
Development of Measurement Method for Thermal Spray Coating Thickness Using Eddy Current Testing
山川智揮, 志垣一也, 林実, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 堺健司
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
33rd
2021
-
Thickness Evaluation of High Manganese Steel Using Low-Frequency Eddy Current Testing
志垣一也, 林実, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 大縄登史男, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
33rd
2021
-
Development of HTS-SQUID Based Measurement System of Localized Magnetic Field for Evaluating Localized Electrochemical Impedance
堺健司, 青木良太, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
68th
1854
-
1854
2021
-
Optimization of applied magnetic field using eddy current testing for thickness evaluation of steel plate with high lift-off
足立祥哉, 川上太聖, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
33rd
2021
-
Development of magnetic sensor probe for high lift-off nondestructive inspection of steel structure
川上太聖, 足立祥哉, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2021
2021
-
Improvement of Detection Reliability for Cancer Cells by Correcting Sensor Sensitivity Using Measurement of pH buffer solution
葭田勇一, XUE Ding, 岩附康平, 井上博文, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2021
-
Optimization of frequency in magnetic measurement for steel structures at a buried position near the ground level
川上太聖, 足立祥哉, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 石川敏之, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2021
2021
-
Development of Terahertz Chemical Microscope for Cross-Sectional Measurement of All-Solid-State Batteries
冨江涼太, 清水雅司, 山口武人, 濱田果周, 寺西貴志, 能勢秀俊, 小林正樹, WANG J., 堺健司, 紀和利彦
電池討論会PDF要旨集(CD-ROM)
62nd
2021
-
A Terahertz Chemical Microscopy
紀和利彦
CSJ Current Review
(
42
)
2021
-
Development of magnetic immunoassay for detection of liquid tumor cells
坪田美咲, 山下慶, 岸本航平, 黒田滉人, WANG J., 堺健司, 紀和利彦
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
45th
2021
-
Evaluation of magnetic particle magnetization characteristics for high sensitivity Magnetic Particle Imaging
野村航大, 山内一輝, 鷲野将臣, 松田哲也, 岡田泰行, 進泰彰, 清野智史, 中川貴, 紀和利彦, 殿岡俊
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
45th
2021
-
Reduction of effects of lift-off by improving applied magnetic field distribution for thickness inspection using magnetism
足立祥哉, 川上太聖, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 石川敏之, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2021
-
Development of differential magnetic measurement system and evaluation of frequency characteristics of magnetic nanoparticles
黒田滉人, 岸本航平, 坪田美咲, 山下慶, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2021
-
Development of a highly-sensitive magnetic measurement system using HTS-SQUID and evaluation of frequency response of magnetic field generated from small current
青木良太, WANG Jin, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 堺健司
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2021
2021
-
バイアス電圧印加によるテラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡検出感度制御
清水雅司, 冨江涼太, 濱田果周, 寺西貴志, 能勢秀俊, 小林正樹, 王しん, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
シンポジウムテラヘルツ科学の最先端講演要旨集
2021
2021
-
Evaluation method independent of plate thickness of ground corrosion of equipment attached to road by extremely low-frequency eddy current testing
川上太聖, 足立祥哉, 林実, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 石川敏之, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2021
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いたリチウムイオン電池電極のインピーダンス測定法の開発—Development of impedance measurement of lithium ion batteries electrode using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
清水 雅司, 藤田 隼人, 王 璡, 堺 健司, 塚田 啓二, 紀和 利彦, 山中 亮治, 寺西 貴志
「センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システム」シンポジウム論文集 電気学会センサ・マイクロマシン部門 [編]
37
4p
2020.10
-
Development of measurement method of ion concentration in extremely small amount solution using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
谷泉克弥, 眞鼻敦也, WANG Jin, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
37
4p
2020.10
-
Monitoring of Different pH Buffer Solutions’ Interaction in Micro Flow Channels Fabricated by PolyDiMethylSiloxane
Ahmed Feroz, Mahana Atsuya, Taniizumi Katsuya, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2020.2
864
-
864
2020.8
-
Histamine concentration measured by a terahertz chemical microscope
Yoshida Yuichi, Sato Kosuke, Sakai Kenji, Tsukada Keiji, Kiwa Toshihiko
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
2020.2
863
-
863
2020.8
-
Nondestructive Evaluation of Inner Defect Generated Inside Copper-alloy-casting Using Low-Frequency Eddy Current Testing
志垣一也, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 堺健司
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
71st
2020
-
Detection of micro metal defects by dual-channel magnetic sensor probe with an excitation wire
小部寛斗, 合田悠斗, 神原匠, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
23rd
2020
-
Effect of annealing temperature on the magnetic response of eddy current testing for hardness evaluation of steel plate
堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
23rd
2020
-
Magnetic noise characteristics of a wide variety of automobiles
齊藤大介, 林実, 王しん, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
44th
2020
-
Effect of Distance between Deformed Bar and Sensor on Corrosion Signal Measured by Unsaturated AC Magnetic Flux Leakage Testing
川上太聖, 林実, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
71st
2020
-
Evaluation of the influence of vehicle environmental noise on magnetic measurement
齊藤大介, 小嵐愛子, 林実, 若林俊輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2020
2020
-
Evaluation method of penetration speed of cosmetic liquid into skins using terahertz technology
紀和利彦
コスメトロジー研究報告
28
2020
-
Highly sensitive magnetic measurement systems using superconducting devices and their applications
塚田啓二, 堺健司, 紀和利彦
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
67th
191
-
191
2020
-
Measurement of concentration of histamine in buffer solution using Terahertz Chemical Microscope for allergy screening
佐藤孝祐, 飯田将弘, 葭田勇一, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
67th
2020
-
Serum influence on magnetic properties of magnetic nanoparticles
山下慶, 平松文太, 神野克也, 綱島健太, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, SAARI Mohd Mawardi Bin
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2020
2020
-
Frequency dependence of magnetic properties of magnetic nanoparticles in liquid phase and solid phase
平松文太, 山下慶, 神野克也, 綱島健太, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2020
2020
-
光触媒のサブピコ秒電位変化の計測実現
紀和利彦
岡山工学振興会ニュース
(
117
)
2020
-
Reduction of Wind Disturbance by Optimizing the Drive Current of Pt Ultra-thin Film Hydrogen Sensor
合田悠斗, 小部寛斗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 近藤健二, 高橋琢哉, 上田尚宏, 塚田啓二
電気学会論文誌 E
140
(
4
)
92
-
96
2020
-
Nondestructive Evaluation of Continuous Welded Rails using Unsaturated AC Flux Leakage Measurements with a Gradiometer
林実, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2020
2020
-
Corrosion Detection of Reinforcing Bar Using Magnetic Flux Leakage Testing
川上太聖, 林実, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
32nd
2020
-
Nondestructive Evaluation of Copper-alloy-casting Using Eddy Current Testing
志垣一也, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 堺健司
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
32nd
2020
-
Improvement of environmental resistance by optimizing the current drive method of Pt ultra-thin film hydrogen sensor
合田悠斗, 小部寛斗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 近藤健二, 高橋琢哉, 上田尚宏, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
36
3p
2019.11
-
Evaluation of quenched area at the edge of steel plate using eddy current testing
堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2019
2019
-
None-Destructive Evaluation of Electrodes of Rechargeable Batteries by Terahertz Technology
紀和利彦, 藤原健太郎, 秋和佑希, 吉川祐未, 寺西貴志, 能勢秀俊, 小林正樹, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
レーザー研究
47
(
1
)
2019
-
極低周波渦電流探傷法による錆で覆われた鋼材の板厚評価
富岡卓哉, 若林俊輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 武藤秀人, 藤野陽三
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2019
2019
-
磁気計測によるアルミニウム合金と鋼の溶接接合の評価
小部寛斗, 合田悠斗, 平田哲朗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2019
2019
-
不飽和交流漏洩磁束法を用いた鉄鋼構造物の亀裂形状の推定
齊藤大介, 林実, 中村喜浩, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2019
2019
-
SQUID磁気免疫検査における磁気を用いた抗原抗体反応の時間短縮
平松文太, 神野克也, 綱島健太, 竹内駿, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2019
2019
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた生体関連物質評価法
Reviewed
紀和利彦, 神谷樹, 飯田将弘, 井上博文, 堺健司, 豊岡伸一, 塚田啓二
日本レーザー医学会誌
39
(
4
)
341
-
346
2019
-
レーザー励起テラヘルツ波を用いた二次電池電極非破壊検査装置の開発
紀和利彦, 寺西貴志
山陽技術雑誌
67
2019
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による微小量溶液中イオン濃度計測
紀和利彦, 前野佑貴, 眞鼻敦也, AHMED Feroz, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
分析化学討論会講演要旨集
79th
2019
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いたin-situリチウムイオン電池評価法
紀和利彦, 秋和佑季, 寺西貴志, 秋和佑季, 能勢秀俊, 小林正樹, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
シンポジウムテラヘルツ科学の最先端講演要旨集
2019
2019
-
磁気免疫検査装置における溶媒による磁気ナノ粒子の磁気特性への影響
平松文太, 神野克也, 綱島健太, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, SAARI Mohd Mawardi Bin, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
70th
2019
-
光触媒のサブピコ秒電位変化の計測実現
紀和利彦
岡山工学振興会ニュース
(
115
)
2019
-
極低周波渦電流探傷法による地際腐食検出性能の向上
若林俊輝, 富岡卓哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
22nd
2019
-
不飽和交流漏洩磁束法による鉄鋼構造物の溶接部欠陥信号の判別
林実, 斉藤大介, 中村喜浩, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
22nd
2019
-
微小金属欠陥が検出可能な磁気センサプローブの開発
小部寛斗, 合田悠斗, 神原匠, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
70th
2019
-
Thickness measurement of severely corroded steel structure using extremely low-frequency eddy current testing
齊藤大介, 林実, 若林俊輝, 富岡卓哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2019
2019
-
Optimization of Pt ultra-thin film pattern for hydrogen sensor
合田悠斗, 平田哲朗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 近藤健二, 高橋琢哉, 上田尚宏, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
35th
2018
-
磁気ナノ粒子を用いたCRPの磁気免疫分析方法
竹内駿, 神野克也, 綱島健太, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 圓福敬二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
96th
2018
-
超伝導コイルと磁気センサを用いた非破壊検査用広周波数帯域磁場検出器の開発
平田哲朗, 合田悠斗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 安達成司, 塚本晃, 田辺圭一, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
96th
2018
-
トンネル磁気抵抗センサを用いた金属材の微小欠陥の検出
神原匠, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 鈴木雄太
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
42nd
2018
-
マルチチャンネル磁気抵抗センサを用いた鉄鋼構造物の亀裂検出
林実, 中村喜浩, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
42nd
2018
-
Evaluation of Localized Electrochemical Impedance Using HTS-SQUID Based Measurement System
Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
79th
2253
-
2253
2018
-
Development of non-destructive testing system using HTS-coil and magnetic sensor for high lift-off crack detection
平田哲朗, 合田悠斗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 安達成司, 塚本晃, 田辺圭一, 塚田啓二
MAGDAコンファレンス講演論文集
27th
2018
-
2次微分検出コイルを用いた鉄鋼構造物の高リフトオフき裂検査法の開発
合田悠斗, 平田哲朗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 田辺圭一, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2018
2018
-
極低周波渦電流探傷法によるチタン下の鋼材の板厚評価
富岡卓哉, 合田剛士, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2018
2018
-
TMRセンサを用いた鉄鋼材の亀裂検出
林実, 中村喜浩, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
21st
2018
-
極低周波渦電流探傷法による鉄鋼構造物の地際腐食検査
若林俊輝, 富岡卓哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
21st
2018
-
SQUID磁気免疫検査装置におけるC反応性タンパクの高感度検出
綱島健太, 神野克也, 竹内駿, 福田行治郎, 藤元佳与, 柴倉美砂子, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 圓福敬二, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
30th
2018
-
エネルギー輸送の違いから見たカーボンナノチューブの通電加熱の効果
中條大樹, 井上寛隆, 黒田泰平, 森本大我, 林拓磨, 徳永知春, 池田直, 横谷尚睦, 藤森和博, 羽田真毅, 西川亘, 山下善文, 紀和利彦, 林靖彦
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
65th
2018
-
The penetration measurement of the skin lotion into the skin using a time-of-flight method
Kuroda Taihei, Morimoto Taiga, Sakai kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
65th
802
-
802
2018
-
グラジオメータを用いた不飽和交流磁束漏洩法によるき裂検出性能
中村喜浩, 林実, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2018
2018
-
SQUID磁気免疫検査装置における磁気マーカを用いたアビジン-ビオチン結合反応の基礎評価
神野克也, 綱島健太, 竹内駿, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 圓福敬二, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
30th
2018
-
超電導薄膜フォーカス板を用いた交流駆動法による磁気抵抗素子の高感度化
合田悠斗, 平田哲朗, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
30th
2018
-
テラヘルツ技術の生体関連試料への応用
紀和利彦
オレオサイエンス
18
(
9
)
2018
-
不飽和交流漏洩磁束法による鉄鋼構造物の亀裂検出と表示方法
林実, 齊藤大介, 中村喜浩, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
69th
2018
-
ヘイセイ 28ネンド シン サンギョウ ソウシュツ ケンキュウカイ 「 ケンキュウ セイカ ホウコクショ 」
(
114
)
12
-
14
2017.9
-
Detection of inner cracks in thick steel plates using non-saturated AC magnetic flux leakage testing with a magnetic resistance gradiometer
K. Tsukada, Y. Majima, Y. Nakamura, T. Yasugi, K. Sakai, T. Kiwa
2017 IEEE International Magnetics Conference, INTERMAG 2017
53
(
11
)
2553
-
2558
2017.8
-
Magnetic AC Impedance Analysis Method Using High-Tc SQUID Based Magnetic Measurement System
Kenji Sakai, Tsubasa Kizu, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
27
(
4
)
274
-
282
2017.6
-
High-Resolution Laser-Assisted Magnetic Nanoparticle Imaging Using a High-T<inf>C</inf> SQUID Magnetometer
Toshihiko Kiwa, Koji Morita, Yasuaki Matsunaga, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Keiji Tsukada
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
27
(
4
)
1108
-
1114
2017.6
-
Magnetic characteristics measurements of ethanol-water mixtures using a hybrid-type high-temperature superconducting quantum-interference device magnetometer
Keiji Tsukada, Yasuaki Matsunaga, Ryota Isshiki, Yuta Nakamura, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa
AIP Advances
7
(
5
)
158
-
162
2017.5
-
Absolute-magnetic-field measurement using nanogranular in-gap magnetic sensor with second-harmonic and liquid-nitrogen-temperature operation
Keiji Tsukada, Takuya Yasugi, Yatsuse Majima, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa
AIP Advances
7
(
5
)
1257
-
1264
2017.5
-
Magnetic method for measuring moisture content using diamagnetic characteristics of water
Tsukada Keiji, Matsunaga Yasuaki, Nakamura Yuta, Isshiki Ryota, Fujimoto Kayo, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko
Measurement Science and Technology
28
(
1
)
3477
-
3487
2017.1
-
低周波磁場を用いた酸化膜付き鋼板の焼入れ状態評価
堺健司, 伊藤嵩展, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
20th
2017
-
磁気スペクトル解析を用いた極低周波渦電流探傷法による腐食鋼構造物の板厚検査
富岡卓哉, 合田剛士, 芳賀勇太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
20th
2017
-
不飽和交流漏洩磁束探傷法の開発と鋼板のき裂検出応用
馬島八世, 八杉拓也, 中村喜浩, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
20th
2017
-
極低周波渦電流探傷法の高速化
富岡卓哉, 合田剛士, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
29th
2017
-
磁気ナノ粒子の溶媒による磁気的挙動変化の高感度測定
竹内駿, 平田哲朗, 一色良太, 中村勇太, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2017
2017
-
極低周波渦電流探傷法によるチタンライニング下の鋼材の板厚評価
富岡卓哉, 合田剛士, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
68th
2017
-
不飽和交流磁束漏洩法によるき裂検出性能
中村喜浩, 馬島八世, SONG NANNAN, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2017
2017
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた電気化学イメージングシステムの開発
藤原健太郎, 川上祐輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
78th
2017
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた磁気ナノ粒子水溶液の異なる溶媒による磁気特性変化の高感度解析
一色良太, 中村勇太, 竹内駿, 平田哲朗, 藤元佳与, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
78th
2017
-
超伝導薄膜フォーカス板を用いた磁気抵抗素子の応答特性
平田哲朗, 中村喜浩, 馬島八世, 天野薫, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
78th
2017
-
超薄膜白金を用いたブリッジ型水素センサ
天野薫, 古川遼, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2017
2017
-
HTS-SQUID磁気特性計測装置の反磁性サンプル回転計測法の高感度化
中村勇太, 竹内駿, 平田哲郎, 一色良太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
68th
2017
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたレーザーアシスト磁気ナノ粒子イメージングの基礎検討
竹内駿, 平田哲朗, 一色良太, 中村勇太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
94th
2017
-
超伝導薄膜フォーカス板を用いた磁気抵抗素子の応答特性
平田哲朗, 中村喜浩, 馬島八世, 天野薫, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
94th
2017
-
HTS-SQUID磁気測定装置を用いたエタノール水溶液の磁気特性評価
中村勇太, 松永恭暁, 一色良太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
64th
2017
-
多重周波数印加磁場を用いた極低周波渦電流探傷検査法による鋼板裏面欠陥検出
合田剛士, 芳賀勇太, 富岡卓哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2017
2017
-
交流変調を用いたTMRセンサの駆動法
中村喜浩, 八杉拓也, 馬島八世, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2017
2017
-
In-vitro penetration assessments of the cosmetic liquid in the bird skin by terahertz-Time-of-Flight method
Arisawa Tsubasa, Morimoto Taiga, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
64th
822
-
822
2017
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた電極評価法の検討
藤原健太郎, 川上祐輝, 日野佑次, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
20th
2017
-
Pt超薄膜を用いたブリッジ型水素センサの開発
天野薫, 古川遼, 井並祥太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2017
2017
-
HTS-SQUID磁気計測装置を用いた磁気ナノ粒子水溶液の溶媒粘度による磁気特性変化評価
一色良太, 中村勇太, 松永恭暁, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
64th
2017
-
Correlation between AC impedance and frequency dependence of magnetic field generated from current measured by HTS-SQUID
Kizu Tsubasa, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
64th
2281
-
2281
2017
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた磁気計測による電気化学インピーダンスの推定
堺健司, 木津翼, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
29th
2017
-
不飽和交流磁束漏洩法(USAC-MFL)による鉄板裏面き裂の検出
中村喜浩, 富岡卓哉, 馬島八世, 合田剛士, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
29th
2017
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による局所電気化学反応計測
紀和 利彦
テラヘルツテクノロジーフォーラム通信
15
2
-
5
2017
-
Current distribution evaluation of dye-sensitized solar cell using HTS-SQUID-based magnetic measurement system
Kenji Sakai, Kohei Tanaka, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
530
113
-
116
2016.11
-
Detection of Inner Corrosion of Steel Construction Using Magnetic Resistance Sensor and Magnetic Spectroscopy Analysis
Keiji Tsukada, Yuta Haga, Koji Morita, Nannan Song, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Weiying Cheng
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
52
(
7
)
2016.7
-
Hybrid Type HTS-SQUID Magnetometer with Vibrating and Rotating Sample
Keiji Tsukada, Koji Morita, Yasuaki Matsunaga, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
26
(
3
)
2016.4
-
Label-free detection of low-molecular-weight samples using a terahertz chemical microscope
Takuya Kuwana, Masahiro Ogawa, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
Applied Physics Express
9
(
4
)
2016.4
-
Compact AC/DC Susceptometer Using a High-Temperature Superconducting Quantum Interference Device
Ryuki Takagi, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
Electronics and Communications in Japan
99
(
3
)
369
-
374
2016.3
-
Improvement of sensitivity of a compact magnetometer by using HTS-SQUID with rotating sample
Daichi Hamasaki, Naohiro Okamoto, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
Electrical Engineering in Japan (English translation of Denki Gakkai Ronbunshi)
194
(
2
)
9
-
14
2016.1
-
Development of a Magnetic Phase Map for Analysis of the Internal Structure of a Spot Weld
Nannan Song, Keisyu Shiga, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
Studies in Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics
41
(
41
)
302
-
311
2016
-
Chloride ion sensor using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Ryosuke Sugai, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines
136
(
4
)
102
-
107
2016
-
Current Distribution Mapping of Dye-sensitize Solar Cell with Various Properties Measured by HTS-SQUID Based Magnetic Measurement System
Sakai Kenji, Kizu Tsubasa, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
77th
2123
-
2123
2016
-
電気化学インピーダンス法を用いた塩素イオンセンサ
菅井良祐, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会論文誌 E
136
(
4
)
2016
-
低周波磁場を用いた漏洩磁束探傷検査法による鋼板裏面の欠陥検出
合田剛士, 芳賀勇太, SONG Nannan, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
67th
2016
-
焼入れによる鋼板の材料特性変化と磁気的非破壊検査法による部分非焼入れ部の判別
堺健司, 伊藤嵩展, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2016
2016
-
磁気ナノ粒子水溶液の磁化特性計測による粒径分布解析
一色良太, 中村勇太, 松永恭暁, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
白金薄膜の水素応答特性評価と水素センサへの応用
天野薫, 古川遼, 井並祥太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
交流変調駆動によるTMRセンサの磁気応答特性
八杉拓也, 馬島八世, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
67th
2016
-
交流変調法を用いた磁気センサ駆動の非破壊検査システムへの応用
馬島八世, 八杉拓也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
67th
2016
-
低周波磁場ベクトルスペクトルを用いた鋼板の板厚検査
芳賀勇太, 合田剛士, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
67th
2016
-
条件が異なる焼入れ部の判別に向けた鋼板の焼入れ温度と磁場応答の関係
伊藤嵩展, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
67th
2016
-
インピーダンス法を用いた塩素センサ用Ag/AgCl電極の評価
天野薫, 菅井良祐, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2016
2016
-
渦電流分布の可視化による表面下欠陥位置及び形状の推定
馬島八世, 八杉拓也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
19th
2016
-
地方創生,中国地方を元気に!4.[岡山発]テラヘルツ計測システム開発プロジェクト
紀和利彦
電子情報通信学会誌
99
(
10
)
2016
-
低周波渦電流探傷法を用いた金属内部欠陥検出法の開発
SONG Nannan, 馬島八世, 八杉拓也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
40th
2016
-
交流変調を用いたTMR磁気センサの駆動
馬島八世, 八杉拓也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
40th
2016
-
In-vitro penetration assessments (Ⅱ) of the cosmetic liquid in the bird skin by terahertz Time of Flight method
Morimoto Taiga, Arisawa Tsubasa, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
77th
944
-
944
2016
-
磁気検査法による鋼材の疲労度評価に向けた材料特性評価と漏洩磁束分布との相関性
堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
19th
2016
-
低周波磁場スペクトルを用いた渦電流探傷検査法による鋼板の板厚評価
合田剛士, 芳賀勇太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
19th
2016
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた電池電極反応分布計測
紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
光アライアンス
27
(
8
)
2016
-
A terahertz chemical microscopy and applications for chemical sensors
紀和利彦
Chemical Sensors
32
(
1
)
2016
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた微少量溶液pH計測
濱田輝, 秋宗広祐, ZHOU Y., 紀和利彦, 堺健二, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
63rd
2016
-
磁気を用いた高感度アルコール濃度計測に向けたSN比の向上
中村勇太, 松永恭暁, 一色良太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いたレクチン糖相互作用のリアルタイム計測
花岡侑樹, 桑名卓也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
超伝導コイルの磁場遮蔽特性を用いた非破壊検査
松永恭暁, 一色良太, 中村勇太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
超薄膜Pt水素センサの熱的安定性の向上と水素に対する温度特性
古川遼, 天野薫, 井並祥太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた磁気ナノ粒子の基礎特性評価
一色良太, 中村勇太, 松永恭暁, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
93rd
2016
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた電気化学反応計測法の開発
川上祐輝, 日野佑次, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
超高感度磁気センサを用いた電流分布計測によるモジュール型色素増感型太陽電池の評価
木津翼, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた微少量溶液pHセンサの開発
ZHOU Y., 秋宗広祐, 濱田輝, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 堺健司
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2016
2016
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた高調波による砂の水分量計測
中村勇太, 松永恭暁, 一色良太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
93rd
2016
-
超薄膜水素センサの安定性の改善
古川遼, 井並祥太, 菅井良祐, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2016
2016
-
交流変調によるMRセンサの駆動法
八杉拓也, 志賀啓秀, 馬島八世, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2016
2016
-
Thermal stability improvement of Pt ultrathin-film hydrogen sensor using TiN
Inami Shota, Furukawa Ryo, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
63rd
347
-
347
2016
-
Application of magnetic sensor with HTS-coil for nondestructive testing
Matsunaga Yasuaki, Morita Koji, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
63rd
2193
-
2193
2016
-
Study for detection of MNP under the skin with the MPI system using HTS-SQUID and near infrared laser irradiation
Morita Koji, Matsunaga Yasuaki, Sakai Kenji, Kiwa Toshihiko, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
63rd
2186
-
2186
2016
-
低周波磁場ベクトルスペクトルによる腐食鋼板の厚み測定
芳賀勇太, 森田洪爾, 合田剛士, 伊藤嵩展, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2016
2016
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡の開発—Development of a terahertz chemical microscopy—特集 テラヘルツ技術の最前線 : 光源と応用の最新動向
紀和 利彦, 堺 健司, 塚田 啓二
Optronics : 光技術コーディネートジャーナル
34
(
9
)
86
-
91
2015.9
-
Non-destructive measurement of water contents in polyethylene films by THz time-domain spectroscopy
Yasumasa Matsuoka, Kenji Sakai Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
2015 11th Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim (CLEO-PR)
1
-
2
2015.8
-
Automatic scanning system for back-side defect of steel structure using magnetic flux leakage method
K. Sakai, K. Morita, Y. Haga, T. Kiwa, K. Inoue, K. Tsukada
2015 IEEE International Magnetics Conference, INTERMAG 2015
1
-
1
2015.7
-
Impedance Evaluation of Hydrogen Sensor Using Ultrathin Platinum Film
Shuzo Takeichi, Yuki Ushita, Ryosuke Sugai, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
40
(
1
)
62
-
72
2015
-
低周波磁場を用いた漏洩磁束探傷検査法による強磁性体材料の板厚評価
芳賀勇太, 森田洪爾, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2015
2015
-
TMRセンサを用いた欠陥の渦電流探傷検査
志賀啓秀, 八杉拓也, 塚本有哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2015
2015
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた高機能サンプル振動型磁化率計の開発
松永恭暁, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 日下瞬, 森田洪爾, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
62nd
2015
-
SQUIDグラジオメータを用いた2ch.磁気計測システムの開発
田中洸平, 糟谷尚平, 石原優一, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2015
2015
-
テラヘルツ波の新時代 テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡=新しい非標識バイオイセンシングツールの開発=
紀和利彦
光アライアンス
26
(
1
)
2015
-
超薄膜水素センサの安定性改善
井並祥太, 菅井良祐, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2015
2015
-
接線2成分磁場合成による電流分布の可視化と欠陥推定への利用
八杉拓也, 志賀啓秀, SONG Nannan, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2015
2015
-
鋼板における部分非焼入れ部の磁気的手法を用いた非破壊検査の検討
堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会秋季講演大会講演概要集
2015
2015
-
非破壊検査に向けた高温超伝導コイルの磁場応答評価
松永恭暁, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 森田洪爾, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2015
2015
-
MPIの高空間分解能化へ向けた高調波比の応用
森田洪爾, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 松永恭暁, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
76th
2015
-
HTS-SQUIDと複数の検出コイルを用いた試料回転型磁気応答計測システムの開発
渡部裕太, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
76th
2015
-
HTS-SQUIDグラジオメーターを用いた磁気計測システムによる色素増感型太陽電池の評価
堺健司, 田中洸平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
76th
2015
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたMPIシステムの赤外光による空間分解能向上の検討
森田洪爾, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 松永恭暁, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
76th
2015
-
Multi-ion detection in solutions using terahertz chemical microscope
Akimune Kosuke, Okawa Yuki, Kiwa Toshihiko, Sakai Kenji, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
62nd
873
-
873
2015
-
テラヘルツ技術の最前線-光源と応用の最新動向-テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡の開発
紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
Optronics
(
405
)
2015
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による生体関連物質相互作用検出
紀和利彦, 秋宗広祐, 周益, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
日本分析化学会年会講演要旨集
64th
2015
-
低周波磁場を用いた鋼板の厚み測定システムの開発
森田洪爾, 芳賀勇太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
66th
2015
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた電流分布測定による各種太陽電池の評価
田中洸平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
66th
2015
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた磁化率計開発
紀和利彦, 堺健司, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2015
2015
-
TMRセンサ高調波信号を用いた非破壊検査システムの開発と画像化
八杉拓也, 志賀啓秀, 塚本有哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
18th
2015
-
自動走行システムを用いたコンテナクレーン鋼構造部の漏洩磁束探傷法による非破壊検査
堺健司, 森田洪爾, 芳賀勇太, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 井上勝美
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
18th
2015
-
AMRセンサアレイを用いた漏洩磁束探傷試験による鋼板の裏面欠陥検出
森田洪爾, 塚本有哉, 志賀啓秀, 芳賀勇太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2015
2015
-
超薄膜Pt/Tiを用いたブリッジ型水素センサの開発
井並祥太, 牛田祐貴, 武市修蔵, 菅井良祐, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
62nd
2015
-
磁気センサアレイを用いた漏洩磁束法による裏面腐食欠陥検査
芳賀勇太, 森田洪爾, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
18th
2015
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡によるD-(+)-マンノースの非標識検出
小川真寛, 中村彰宏, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
62nd
2015
-
Stabilization method for signal drifts in terahertz chemical microscopy.
International journal
Toshihiko Kiwa, Kenji Sakai, Keiji Tsukada
Optics express
22
(
2
)
1330
-
5
2014.1
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた電解質中イオン輸送の可視化
紀和利彦, 糟谷尚平, 宮崎真吾, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
61st
2014
-
Magnetic Relaxation Measurement Using HTS-SQUID Based Rotating Sample Magnetometer with High Sensitivity
堺健司, 岡本直大, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
113
(
401(SCE2013 35-57)
)
2014
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた磁気応答計測システムの高感度化による水分量評価への応用
堺健司, 日下瞬, 岡本直大, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2014
2014
-
トンネル型磁気抵抗素子を用いた裏面欠陥非破壊検査
塚本有哉, 志賀啓秀, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 西川卓男, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
26th
2014
-
渦電流探傷検査法を用いたスポット溶接の検査法の開発
志賀啓秀, 塚本有哉, SONG Nannan, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電磁力関連のダイナミクスシンポジウム講演論文集
26th
2014
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた小型AC/DC磁化率計の研究開発
森田洪爾, MOHD Mawardi, 高木竜輝, 石原優一, 日下瞬, 塚本有哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2014
2014
-
HTS-SQUIDグラジオメータを用いた太陽電池評価システムの開発
田中洸平, 宮崎真伍, 糟谷尚平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2014
2014
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた磁気計測システムの高精度化と水分量計測への応用
堺健司, 渡部裕太, 岡本直大, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
MAGDAコンファレンス講演論文集
23rd
2014
-
スポット溶接内部構造解析用3Dマップの開発
SONG Nannan, 塚本有哉, 志賀啓秀, 原田大地, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, CHENG Weiying, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2014
2014
-
磁場分布自動計測システムを用いた鋼材の疲労度評価の検討
堺健司, 秋山貴俊, 紀和利彦, 井上勝美, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2014
2014
-
漏洩磁束探傷法を用いた鋼構造部内部腐食の検出
堺健司, 秋山貴俊, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2014
2014
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた電解質中イオン輸送の可視化(II)
紀和利彦, 田中洸平, 糟谷尚平, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
75th
2014
-
白金超薄膜を用いたブリッジ型水素センサ
牛田祐貴, 武市修蔵, 菅井良祐, 井波祥太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
65th
2014
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による燃料電池の触媒反応解析
古礒和樹, 日下鉄也, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
75th
2014
-
Development and Application of a Compact Rotating-sample Magnetometer Using HTS-SQUID
堺健司, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
低温工学
49
(
7
)
2014
-
HTS-SQUID回転型磁化率計の高感度化の研究
渡部裕太, 岡本直大, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2014
2014
-
直冷式HTS-SQUIDを用いた太陽電池の光応答特性評価システムの開発
田中洸平, 糟谷尚平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2014
2014
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた高精度磁化率計の開発と水溶液中の磁気ナノ粒子への応用
森田洪爾, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 石原優一, 日下瞬, 塚本有哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2014
2014
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた磁化率計の複合型AC/DC検出ユニットの最適化
SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 森田洪爾, 石原優一, 日下瞬, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
75th
2014
-
高感度磁気センサの非破壊検査への応用 磁気抵抗効果センサを用いた非破壊検査
紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
非破壊検査
63
(
11
)
2014
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた試料回転式磁化率計の試料形状最適化による高感度計測法の検討
堺健司, 岡本直大, 渡部裕太, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2014
2014
-
超薄膜Pt/Tiを用いたブリッジ型水素センサの開発
菅井良祐, 武市修蔵, 牛田祐貴, 井並祥太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
31st
2014
-
AC/DC高温超伝導SQUID磁化率計による水溶液中の酸化鉄ナノ粒子の磁気特性計測
SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 塚本有哉, 石原優一, 日下瞬, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
61st
2014
-
保温材下配管外面欠陥の磁気的検査装置の開発
原拓也, 春日基志, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
38th
2014
-
TMRセンサを用いた裏面欠陥の漏洩磁束探傷検査
志賀啓秀, 塚本有哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 西川卓男, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
38th
2014
-
三層鋼板スポット溶接の磁気を用いた非破壊検査
原田大地, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
非破壊検査
63
(
9
)
2014
-
Non-destructive testing to inner water of PE film by THz-TDS
Matsuoka Yasumasa, Kiwa Toshihiko, Sakai Kenji, Tsukada Keiji
JSAP Annual Meetings Extended Abstracts
75th
817
-
817
2014
-
磁場を用いた保温材下配管の外面欠陥検出と位置特定の検討
堺健司, 春日基志, 橋本源基, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 河部俊英
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
17th
2014
-
産業応用に向けたテラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡の開発
紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
農業食料工学会誌
76
(
3
)
2014
-
Optimization of the Detection Technique for a Vibrating-Sample Magnetometer Using High-T-c SQUID
Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY
23
(
3
)
1600204
2013.6
-
テラヘルツケミカル顕微鏡と応用開拓
紀和 利彦
O plus E
35
(
2
)
147
-
151
2013
-
Compact rotating-sample magnetometer for relaxation phenomenon measurement using HTS-SQUID
Kenji Sakai, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
23
(
3
)
1601904
2013
-
Magnetic detection of currents in an electrolytic cell using high-T <inf>C</inf> SQUID
Toshihiko Kiwa, Yohei Fukudome, Shingo Miyazaki, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Akira Tsukamoto, Seiji Adachi, Keiichi Tanabe, Akihiko Kandori, Keiji Tsukada
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
23
(
3
)
1600804
2013
-
Magnetic evaluation of a solar panel using HTS-SQUID
Toshihiko Kiwa, Yohei Fukudome, Shingo Miyazaki, Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Keiji Tsukada
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
494
(
15
)
195
-
198
2013
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いたDC/AC複合小型磁化率計の開発
高木竜輝, MOHD Mawardi Saari, 石原優一, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
87th
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた磁気緩和測定システムの高精度化
堺健司, 岡本直大, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2013
2013
-
Optimized Rotating-sample Magnetometer Using HTS-SQUID and its Application to Moisture Content Evaluation
堺健司, 日下瞬, 岡本直大, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
113
(
232(SCE2013 19-34)
)
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDグラジオメータを用いた太陽電池直流電流計測システムの開発
宮崎真伍, 糟谷尚平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達誠司, 田辺圭一, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
74th
2013
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いたDC・AC複合小型磁化率計の開発
石原優一, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
37th
2013
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた小型磁化率計による水分量測定
日下瞬, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
37th
2013
-
Development of AC-magnetometer Using HTS-SQUID and Optimization of Measurement System
堺健司, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
113
(
149(SCE2013 10-18)
)
2013
-
THz波ケミカル顕微鏡による燃料電池の触媒反応解析システムの開発
日下鉄也, 萩原隆文, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
74th
2013
-
HTS-SQUID磁気計測による太陽電池電気特性評価
宮崎真伍, 福留陽平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会大会講演論文集
2013
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたサンプル回転方式小型磁気計測計による磁気緩和測定
浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2013
(
2
)
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた電気磁気化学計測システムの開発(II)
紀和利彦, 福留陽平, 宮崎真伍, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
60th
2013
-
白金メタマテリアル構造の水素応答評価
園拓也, 篠宮光博, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
60th
2013
-
Highly-sensitive measurement technique of a compact magnetometer using HTS-SQUID and rotating sample
堺健司, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
112
(
408(SCE2012 25-38)
)
2013
-
漏洩磁束探傷法を用いた鋼板の疲労度検出システムの開発
堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 井上勝美
表面探傷シンポジウム講演論文集
16th
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた試料回転式小型磁化率計のシステム改善による高感度化
堺健司, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会大会講演論文集
2013
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDによる試料回転式小型磁化率計を用いた水分量計測
堺健司, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
60th
2013
-
高感度計測法を用いた高温超伝導SQUID磁化率計
SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会春季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
60th
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたサンプル回転型小型磁化率計の開発
岡本直大, 浜崎大地, SAARI M. M., 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
37th
2013
-
三層鋼板スポット溶接の磁気を用いた非破壊検査
原田大地, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2013
2013
-
スポット溶接内部構造解析用磁気位相マップの開発
SONG Nannan, 塚本有哉, 志賀啓秀, 原田大地, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, CHENG Weiying, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2013
2013
-
HTS-SQUID磁気特性評価装置におけるAC磁場検出方法の最適化
石原優一, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡によるイオン計測システムの開発
大川裕貴, 萩原隆文, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
74th
2013
-
テラヘルツ波光源と応用 テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡と応用開拓
紀和利彦
O plus E
(
399
)
2013
-
テラヘルツ波による生体関連物質化学反応センシング
紀和利彦, 萩原隆文, 大村健, 高橋慎治, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
74th
2013
-
HTS-SQUID磁気特性評価装置における高調波検波方式の研究
塚本有哉, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
高速スキャン型テラヘルツ分光ユニットの雑音特性
難波勇馬, 園拓也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
テラヘルツ電磁波を用いたSiGe薄膜評価システムの開発
中村彰宏, 大村健, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
回転型HTS-SQUID磁化率計の高感度検出法の研究
岡本直大, 浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたサンプル回転方式小型磁化率計の高感度化
浜崎大地, 岡本直大, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
74th
2013
-
保温材下配管外面欠陥の磁気的検査装置の開発
春日基志, 橋本源基, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
64th
2013
-
白金薄膜抵抗の構造変化による水素応答評価とブリッジ型水素センサの開発
牛田祐貴, 奥井貴博, 武市修蔵, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
64th
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた太陽電池の光応答特性分布解析
糟谷尚平, 宮崎真伍, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた磁気特性評価装置によるモルタル水分量測定
日下瞬, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
白金薄膜の表面構造による水素応答評価
武市修蔵, 奥井貴博, 牛田祐貴, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
30th
2013
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたAC/DC複合小型磁化率計の開発
高木竜輝, 石原優一, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会秋季学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
74th
2013
-
白金薄膜抵抗を用いたブリッジ回路型水素センサの開発
牛田祐貴, 奥井貴博, 武市修蔵, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
30th
2013
-
低周波磁場を用いた金属疲労画像化装置
秋山貴俊, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
64th
2013
-
保温材下配管外面欠陥の磁気的検査装置の開発-その3
橋本源基, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2013
2013
-
テラヘルツ波を用いた生体関連イオン計測手法の開発
大川裕貴, 萩原隆文, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた寒天ゲル膜の評価
中村彰宏, 大村健, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本分光学会テラヘルツ分光部会シンポジウム講演要旨集
2013
2013
-
THz波ケミカル顕微鏡による発電中の燃料電池触媒反応解析
日下鉄也, 萩原隆文, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理・物理系学会中国四国支部合同学術講演会講演予稿集
2013
2013
-
テラヘルツ波バイオ検査装置の開発と現状
紀和利彦
日本分光学会テラヘルツ分光部会シンポジウム講演要旨集
2013
2013
-
白金ナノ薄膜の水素応答評価
武市修蔵, 奥井貴博, 牛田祐貴, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
64th
2013
-
Compact Vibrating-Sample Magnetometer using High-T_c SQUID and Sample Shape Dependency
SAARI Mohd Mawardi, TAKAGI Ryuuki, SAKAI Kenji, KIWA Toshihiko, TSUKAMOTO Akira, ADACHI Seiji, TANABE Keiichi, KANDORI Akihiko, TSUKADA Keiji
Technical report of IEICE. SCE
112
(
138
)
31
-
36
2012.7
-
Work function shifts of catalytic metals under hydrogen gas visualized by terahertz chemical microscopy.
International journal
Toshihiko Kiwa, Takafumi Hagiwara, Mitsuhiro Shinomiya, Kenji Sakai, Keiji Tsukada
Optics express
20
(
11
)
11637
-
42
2012.5
-
Development of a compact moving-sample magnetometer using high-Tc superconducting quantum interference device
Mohd Mawardi Saari, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa, Akira Tsukamoto, Seiji Adachi, Keiichi Tanabe, Akihiko Kandori, Keiji Tsukada
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics
51
(
4 PART 1
)
046601
2012.4
-
Electric Characteristics of a Loop in Which Two Junctions between a Catalytic Metal and a Noncatalytic Metal Are under Different Hydrogen Gas Concentrations
Keiji Tsukada, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa
APPLIED PHYSICS EXPRESS
5
(
3
)
034102
2012.3
-
Changes in work function and electrical resistance of Pt thin films in the presence of hydrogen gas
Keiji Tsukada, Hirotsugu Inoue, Fumiya Katayama, Kenji Sakai, Toshihiko Kiwa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics
51
(
1
)
015701
2012.1
-
Non-destructive evaluation system using high-Tc SQUID
紀和利彦, 福留陽平, 堺健司, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥昭彦, 塚田啓二
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
111
(
418(SCE2011 19-26)
)
11
-
16
2012
-
Biosensing by a terahertz chemical microscope.
紀和利彦
応用物理
81
(
4
)
298
-
303
2012
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による抗原非標識定量計測
高橋慎治, 天満陽, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2012
2012
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた交流磁気特性計測システムの開発
山口嘉竜, 前田敏志, 浜崎大地, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
59th
2012
-
薄膜抵抗型水素センサの開発
奥井貴博, 片山文哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2012
(
3
)
2012
-
参照電極が不要なイオンセンサの応答機構解析
山本貴文, 小森達也, 小田和代, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2012
(
3
)
2012
-
Characterization of New Structural Sodium Ion Sensor using Electrochemical Impedance Method
小森達也, 山本貴文, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-12
(
1-16
)
2012
-
異なる白金薄膜構造をもつ抵抗変化式水素センサの応答解析
奥井貴博, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
29th
2012
-
保温材下配管外面欠陥の磁気的検査装置の開発-その2
橋本源基, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2012
2012
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた磁気緩和測定用小型磁化率計の開発
堺健司, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 浜崎大地, 紀和利彦, 円福敬二, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
73rd
2012
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた直流磁化率計の高感度計測法
SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
73rd
2012
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた電気磁気化学計測システムの開発
紀和利彦, 宮崎真伍, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
73rd
2012
-
完全個体型イオンセンサの応答解析とマルチイオンセンサの集積化および性能評価
山本貴文, 小森達也, 小田和代, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
29th
2012
-
レーザー励起THz顕微鏡によるSiGeウェハの非破壊検査
大村健, 紀和利彦, 山下善文, 堺健司, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
59th
2012
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡によるタンパク質結合検出
紀和利彦
分光研究
61
(
1
)
2012
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた太陽電池の電気特性分布計測システムの自動化
福留陽平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達誠司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
59th
2012
-
気密THz-TDSユニットの開発
能勢秀俊, 篠宮光博, 門脇信傑, 児島孝則, 小林正樹, 奥野雅史, 紀和利彦
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
59th
2012
-
小型ピックアップコイル結合型HTS-SQUIDを用いた太陽電池特性評価システムの開発
紀和利彦, 福留陽平, 宮崎真伍, 高木竜輝, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
86th
2012
-
保温材下配管外面欠陥の磁気的検査装置の開発
橋本源基, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2012
2012
-
磁束透過法によるスポット溶接欠陥検査
原田大地, 塚田啓二, 紀和利彦, 堺健司
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2012
2012
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた振動型小型磁化率計の開発
高木竜輝, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2012
2012
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたサンプル回転型直流磁化率計の開発
浜崎大地, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2012
2012
-
ECTを用いたスポット溶接欠陥の内部構造解析
原田大地, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2012
2012
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡によるイオン反応の可視化
萩原隆文, 篠宮光博, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
63rd
2012
-
HTS-SQUID磁気計測による太陽電池電気特性評価
宮崎真伍, 福留陽平, SAARI Mohd Mawardi, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2012
2012
-
Evaluation system for catalytic reactions using terahertz chemical microscope
萩原隆文, 篠宮光博, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-12
(
1-16
)
43
-
46
2012
-
Mapping system of Chemical Reactions using Terahertz Chemical Microscope
紀和利彦, 高橋慎司, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-12
(
1-16
)
2012
-
Differential conductivity mapping of solar panels using a high-T <inf>C</inf> superconductor SQUID
T. Kiwa, S. Maeda, K. Miyake, N. Kataoka, A. Tsukamoto, S. Adachi, K. Tanabe, A. Kandori, K. Tsukada
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
471
(
21-22
)
1238
-
1241
2011.11
-
A magnetic flux leakage method using a magnetoresistive sensor for nondestructive evaluation of spot welds
Keiji Tsukada, Mitsuteru Yoshioka, Toshihiko Kiwa, Yoshinobu Hirano
NDT and E International
44
(
1
)
101
-
105
2011.1
-
テラヘルツを用いたバイオセンシング
紀和利彦, 天満陽, 橋本陽平, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
日本分光学会赤外ラマン分光部会シンポジウム
6th
2011
-
High-TCSQUIDを用いた太陽電池パネル非破壊検査
紀和利彦, 前田敏志, 三宅康介, 片岡伸夫, 堺健司, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
58th
2011
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた小型磁化率計の開発
堺健司, MOHAMADO Mawarudei, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
58th
2011
-
Development of All-solid-state Multi Ion Sensor without a Reference Electrode
小田和代, 小森達也, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-11
(
1-24
)
2011
-
Development of thin film resistance type Hydrogen sensor
片山文哉, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会マイクロマシン・センサシステム研究会資料
MSS-11
(
1-7.9-12.14-21
)
55
-
58
2011
-
漏洩磁束探傷検査法を用いたスポット溶接欠陥検査用画像化装置の開発
三宅康介, 吉岡光輝, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 平野佳伸, 松元光明
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2011
(
2
)
2011
-
High-TcSQUIDを用いた太陽電池パネル接合容量分布計測
紀和利彦, 福留陽平, 前田敏志, 堺健司, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2011
-
高温超電導SQUIDを用いた小型磁化率計の開発
MAWARDI Mohd, 前田敏志, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2011
-
ダブルパルス検出法によるテラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡のノイズキャンセル
天満陽, 紀和利彦, 門脇信傑, 小林正樹, 堺健司, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
72nd
2011
-
保温断熱配管の磁気的非破壊検査方法の開発
土井貴範, 三宅康介, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2011
2011
-
テラヘルツ波面制御素子の放射パターン制御評価
篠宮光博, 岡田啓太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本分光学会テラヘルツ分光部会シンポジウム講演要旨集
2011
2011
-
High-TcSQUIDを用いた太陽電池パネル電気特性分布計測
紀和利彦, 前田敏志, 三宅康介, 堺健司, 塚田啓二, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
84th
2011
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた試料回転式小型磁化率計の開発
堺建司, MOHD Mawardi, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
85th
2011
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた交流磁化率計の開発
前田敏志, 山口嘉竜, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦
低温工学・超電導学会講演概要集
84th
2011
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた太陽電池の電気特性分布計測
福留陽平, 前田敏志, 紀和利彦, 堺健司, 塚本晃, 安達誠司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2011
2011
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いたヘルムホルツ型交流磁化率計の開発
山口嘉竜, 前田敏志, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2011
2011
-
交流インピーダンス法を用いた新型イオンセンサの特性評価
小森達也, 小田和代, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
62nd
2011
-
透過磁場検出によるスポット溶接検査法の開発
澤井勇人, 三宅康介, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 平野佳伸
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
62nd
2011
-
低周波磁場を用いたスポット溶接の非破壊検査
堺健司, 三宅康介, 紀和利彦, 平野佳伸, 松元光明, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2011
2011
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡とバイオセンシング
紀和利彦
日本分光学会テラヘルツ分光部会シンポジウム講演要旨集
2011
2011
-
テラヘルツ波放射制御デバイス磁気特性評価
篠宮光博, 岡田啓太, 堺健司, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2011
2011
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた層流イメージング
橋本陽平, 近藤洋輔, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
58th
2011
-
ダブルパルス検出法によるテラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡の高感度計測
天満陽, 近藤洋輔, 紀和利彦, 門脇信傑, 小林正樹, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
58th
2011
-
テラヘルツ電磁波技術研究会
川瀬 晃道, 紀和 利彦
應用物理
79
(
9
)
845
-
845
2010.9
-
Terahertz electronics
79
(
8
)
697
-
699
2010.8
-
Terahertz chemical microscope for label-free detection of protein complex
Toshihiko Kiwa, Yousuke Kondo, Yuji Minami, Iwao Kawayama, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
Applied Physics Letters
96
(
21
)
2010.5
-
おわりに
紀和 利彦
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
2010.1
176
-
176
2010.3
-
Dual-Gate field-effect transistor hydrogen gas sensor with thermal compensation
Keiji Tsukada, Masatoshi Kariya, Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironobu Yamada, Tsuneyoshi Maehara, Tadayoshi Yamamoto, Shinsuke Kunitsugu
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics
49
(
2 Part 1
)
2010.2
-
Evaluation of the sensitivity of hydrogen sensors covered with polytetrafluoroethylene as a protective membrane for humidity
Koji Fujii, Hirotsugu Inoue, Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines
130
(
8
)
401
-
406
2010
-
Development and evaluation of a Pt/Ti-FET-type hydrogen sensor
Masatoshi Kariya, Kouhei Mizuhara, Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Toshihiko Kiwa, Shinsuke Kunitsugu, Keiji Tsukada
IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines
130
(
8
)
407
-
411
2010
-
セキュアライフを支えるテラヘルツ波技術 テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による非標識バイオセンシング
紀和利彦
Bio Industry
27
(
10
)
14
-
19
2010
-
Detectionofback-sidepitonaferrousplatebymagneticfluxleakagemethod with analyzingmagneticfieldvector
Keiji Tsukada, Mitsuteru Yoshioka, Yoshihiko Kawasaki, Toshihiko Kiwa
NDT & E International
43
(
4
)
323
-
328
2010
-
テラヘルツ波センシングプレート封入型検査セルの開発
紀和利彦
村田学術振興財団年報
(
24
)
2010
-
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TYPE MICRO ION SENSOR WITHOUT A REFERENCE ELECTRODE
井上豊崇, 小田和代, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
Chemical Sensors
2010
(
3
)
2010
-
溶接部内部欠陥検出用磁気センサアレイプローブの開発
三宅康介, 萬治寧大, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 櫻本昌宏, 井上勝美
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2010
(
2
)
2010
-
PROTON-PUMPING GATE STRUCTURE FOR A FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR TYPE HYDROGEN SENSOR
山口富治, 假谷正敏, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
Chemical Sensors
26
(
Supplement A
)
2010
-
PROTON-PUMPING GATE STRUCTURE FOR A FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR TYPE HYDROGEN SENSOR
山口富治, 假谷正敏, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
Chemical Sensors
77th
(
Supplement A
)
2010
-
Hydrogen Response Characteristic of Platinum Thin Film
水原宏平, 片山文哉, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-10
(
1-6.8-14
)
17
-
21
2010
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた磁気特性計測システムの開発
前田敏志, 片岡伸夫, 紀和利彦, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 神鳥明彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
71st
2010
-
HTS-SQUIDを用いた太陽電池の微分抵抗特性分布測定
紀和利彦, 前田敏志, 三宅康介, 片岡伸夫, 塚本晃, 安達成司, 田辺圭一, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
71st
2010
-
低周波磁場を用いた金属疲労検査法の開発
三宅康介, 吉岡光輝, 紀和利彦, 櫻本昌宏, 井上勝美, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
34th
2010
-
スポット溶接評価用漏洩磁束探傷検査法
吉岡光輝, 三宅康介, 紀和利彦, 平野佳伸, 松本光明, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2010
2010
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡によるpH分布評価応用
近藤洋輔, 橋本陽平, 天満陽, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2010
2010
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡のμ-TAS測定
橋本陽平, 近藤洋輔, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
71st
2010
-
テラヘルツ波面制御デバイスの開発と評価
別府慶治, 杉本武史, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
57th
2010
-
テラヘルツ波面制御デバイスの開発
別府慶治, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
61st
2010
-
触媒金属ゲートFETにおける応答メカニズムの解析
井上大嗣, 片山文哉, 水原宏平, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
27th
2010
-
FET型センサを用いた新型酸素センサの開発
切明大輔, 片山文哉, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
センサ・マイクロマシンと応用システムシンポジウム(CD-ROM)
27th
2010
-
保温断熱配管の磁気的非破壊検査方法の開発
三宅康介, 吉岡光輝, 土井貴範, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 河部俊英, 藤田理絵, 花口正典
日本非破壊検査協会講演大会講演概要集
2010
2010
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた植物断面のpH分布イメージング
近藤洋輔, 南祐治, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集(CD-ROM)
57th
2010
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡の高感度化に向けたダブルパルス検出法の開発
天満陽, 近藤洋輔, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会中国四国支部・日本物理学会中国支部・四国支部・日本物理教育学会中国四国支部支部学術講演会講演予稿集
2010
2010
-
A novel ion sensor without a reference electrode
Keiji Tsukada, Fumiyuki Kobayashi, Toyotaka Inoue, Toshihiko Kiwa
Sensor Letters
7
(
6
)
1163
-
1166
2009.12
-
Magnetic thickness gauge using a Fourier transformed eddy current technique
Toshihiko Kiwa, Takayuki Hayashi, Yoshihiko Kawasaki, Hironobu Yamada, Keiji Tsukada
NDT and E International
42
(
7
)
606
-
609
2009.10
-
Non-contact thickness gauge for conductive aterials using HTS SQUID system
Toshihiko Kiwa, Hideaki Tahara, Etsuro Miyake, Hironobu Yamada, Keiji Tsukada
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
19
(
3
)
801
-
803
2009.6
-
Magnetic image detection of the stainless-steel welding part inside a multi-layered tube structure
Takayuki Hayashi, Yoshihiko Kawasaki, Hironobu Yamada, Toshihiko Kiwa, Masaji Tamazumi, Keiji Tsukada
NDT and E International
42
(
4
)
308
-
315
2009.6
-
Highly sensitive measurement of moisture content using HTS-SQUID
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hideaki Tahara, Etsuro Miyake, Hironobu Yamada, Akira Tsukamoto, Akihiko Kandori
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
19
(
3
)
878
-
881
2009.6
-
Hydrogen selectivity of a proton-pumping gate FET hydrogen sensor in an AC modulation mode
Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Masanori Takisawa, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironobu Yamada, Keiji Tsukada
IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines
129
(
4
)
110
-
114
2009
-
Measurement of pH in fluidic chip using a terahertz chemical microscope
Toshihiko Kiwa, Shohei Oka, Yuji Minami, Iwao Kawayama, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines
129
(
7
)
221
-
224
2009
-
Temperature control and packaging optimization of the integrated hydrogen sensor
Kousuke Tsubota, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironobu Yamada, Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Yohei Kondo, Hirofumi Imajo, Tsutomu Hondo, Tunetoshi Maehara, Tadayoshi Yamamoto, Keiji Tsukada
IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines
129
(
9
)
2
-
282
2009
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた固定化酵素反応イメージング
南祐治, 岡昇平, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
56th
(
3
)
2009
-
Development of a nondestructive testing system using HTS-SQUID with a normal pickup-coil
MIYAKE Etsuro, KIWA Toshihiko, TSUKADA Keiji, TSUKAMOTO Akira
81st
232
2009
-
DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW TYPE MICRO ION SENSOR WITHOUT A REFERENCE ELECTRODE
井上豊崇, 小田和代, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
Chemical Sensors
25
(
Supplement B
)
2009
-
フーリエ変換過流探傷法による鉄鋼板厚の非破壊検出
林孝之, 林孝之, 川崎喜彦, 吉岡光輝, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 井上勝美, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
33rd
2009
-
磁気を用いたモルタルの水分含有量の測定方法
片岡伸夫, 増田康孝, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 尾藤良孝, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
33rd
2009
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いたアビジン-ビオチン結合の検出
近藤洋輔, 南祐治, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
70th
(
3
)
2009
-
ガス透過膜の水素センサへの適用
藤井浩二, 山口富治, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2009
(
3
)
2009
-
プロトンポンピングゲートFETをベースとした集積化水素ガスセンサの開発
山口富治, 坪田公輔, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 近藤洋平, 今城啓文, 本藤勉, 前原経利, 山本忠義
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2009
(
3
)
2009
-
低周波磁気ベクトル解析による鉄鋼板厚みの非破壊検出方法
林孝之, 林孝之, 川崎喜彦, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 井上勝美, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会大会講演概要集
2009
2009
-
印加磁場直交配置型HTS-SQUID非破壊検査装置の開発
紀和利彦, 三宅悦朗, 山田博信, 塚本晃, 塚田敬二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
70th
(
1
)
2009
-
低周波磁場を用いた漏洩磁束探傷試験
吉岡光輝, 川崎喜彦, 紀和利彦, 塚出啓二
電気・情報関連学会中国支部連合大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
60th
2009
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いたフーリエ型パルス渦流探傷法による金属板の欠陥検出
三宅悦朗, 田原秀哲, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
56th
(
1
)
2009
-
Pt/Ti二層ゲートFET型水素センサの空気雰囲気での水素応答特性
假谷正敏, 山口富治, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二, 國次真輔
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2009
(
3
)
2009
-
Analysis of response mechanism of a proton-pumping gate FET hydrogen gas sensor in air
T. Yamaguchi, M. Takisawa, T. Kiwa, H. Yamada, K. Tsukada
Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical
133
(
2
)
538
-
542
2008.8
-
Chemical sensing plate with a laser-terahertz monitoring system.
International journal
Toshihiko Kiwa, Junichi Kondo, Shohei Oka, Iwao Kawayama, Hironobu Yamada, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
Applied optics
47
(
18
)
3324
-
7
2008.6
-
Magnetic measurement of the moisture content in soil: Diamagnetic measurement with the presence of ferromagnetic material
Keiji Tsukada, Yasutaka Masuda, Yudai Ishihara, Toshihiko Kiwa
Applied Physics Express
1
(
6
)
0670081
-
0670083
2008.6
-
Magneto-electrical cyclic voltammetry for visualization of current distribution in the electrolyte
K. Tsukada, F. Kobayashi, H. Arai, T. Kiwa
Electrochemistry Communications
10
(
6
)
938
-
942
2008.6
-
Difference in the detection limits of flaws in the depths of multi-layered and continuous aluminum plates using low-frequency eddy current testing
Hironobu Yamada, Teruki Hasegawa, Yudai Ishihara, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada
NDT and E International
41
(
2
)
108
-
111
2008.3
-
Detection of the weak magnetic properties change of stainless-steel welding parts by low frequency magnetic imaging
Takayuki Hayashi, Hironobu Yamada, Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada, Masaji Tamazumi
Journal of Applied Physics
103
(
7
)
07E923
2008
-
Redox reactions of enzymes measured by terahertz chemical microscope
Toshihiko Kiwa, Jyunichi Kondo, Iwo Kawayama, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
33rd International Conference on Infrared and Millimeter Waves and the 16th International Conference on Terahertz Electronics, 2008, IRMMW-THz 2008
594
-
+
2008
-
磁場計測による電解質溶液中の電流評価
小林史幸, 新井裕之, 萬治寧大, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2008
(
2
)
2008
-
低周波磁気を用いたステンレス多層配管内の溶接部の新しい非破壊検出方法
林孝之, 林孝之, 川崎喜彦, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 玉積正司, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会大会講演概要集
2008
2008
-
極低周波磁気を用いた鉄板溶接部の内部欠陥検査法
長谷川照起, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 井上勝美, 玉積正司, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会大会講演概要集
2008
2008
-
パルス渦流探傷を用いたリフトオフの影響を受けない金属板厚み検査法の開発
川崎喜彦, 林孝之, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
32nd
2008
-
低周波磁気検査によるステンレス多層配管中の溶接部の検出
林孝之, 林孝之, 川崎喜彦, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 玉積正司, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
32nd
2008
-
HTS-SQUID渦流探傷法による金属厚み検査装置の開発
紀和利彦, 田原秀哲, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
69th
(
1
)
2008
-
各種ガスによるプロトンポンピングゲート水素センサのゲート部のインピーダンス変化
滝澤正教, 山口富治, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2008
(
3
)
2008
-
低周波磁気イメージングシステムによるステンレス溶接欠陥の非破壊検査
林孝之, 林孝之, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 玉積正司, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2008
(
2
)
2008
-
フーリエ型パルス渦流探傷法による金属板厚検査法の開発
紀和利彦, 川崎喜彦, 林孝之, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
日本非破壊検査協会大会講演概要集
2008
2008
-
磁気による砂の水分含有量の測定方法
増田康孝, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本磁気学会学術講演概要集
32nd
2008
-
砂の水分量の新しい磁気計測方法
塚田啓二, 増田康孝, 石原雄大, 紀和利彦
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
55th
(
1
)
2008
-
交流変調時におけるプロトンポンピングゲートFET型水素センサの応答特性評価
山口富治, 滝澤正教, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2008
(
3
)
2008
-
高温超伝導SQUIDを用いた高感度水分含有量測定システムの開発
田原秀哲, 三宅悦朗, 窪田篤, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
55th
(
1
)
2008
-
低周波渦流探傷検査システムの鉄板溶接部評価への適用
長谷川照起, 石原雄大, 林孝之, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2008
(
2
)
2008
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡によるガス選択検出手法の開発
小野坂宏之, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 川山巌, 斗内政吉
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2008
(
3
)
2008
-
THz波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いた酵素反応検出
紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
69th
(
3
)
2008
-
THz波ケミカル顕微鏡を用いたガス触媒評価手法の開発
紀和利彦, 小野坂宏之, 川山巌, 山田博信, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
55th
(
3
)
2008
-
テラヘルツ波ケミカル顕微鏡による流路内化学濃度分布イメージング
岡昇平, 近藤純一, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
55th
(
3
)
2008
-
A terahertz chemical microscope to visualize chemical concentrations in microfluidic chips
Toshihiko Kiwa, Shohei Oka, Junichi Kondo, Iwao Kawayama, Hironobu Yamada, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2: Letters
46
(
41-44
)
L1052
-
L1054
2007.11
-
A proton pumping gate field-effect transistor for a hydrogen gas sensor
Keiji Tsukada, Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Toshihiko Kiwa
IEEE Sensors Journal
7
(
9
)
1268
-
1269
2007.9
-
Fourier-transformed eddy current technique to visualize cross-sections of conductive materials
Toshihiko Kiwa, Tomoaki Kawata, Hironobu Yamada, Keiji Tsukada
NDT and E International
40
(
5
)
363
-
367
2007.7
-
Magnetic measurement of moisture content of grain
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
43
(
6
)
2683
-
2685
2007.6
-
Detection of photomixing signals with a YBCO Josephson junction coupled to a coplanar waveguide
Iwao Kawayama, Ryuhei Kinjo, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
17
(
2
)
321
-
323
2007.6
-
Oxygen interference mechanism of platinum-FET hydrogen gas sensor
T. Yamaguchi, T. Kiwa, K. Tsukada, K. Yokosawa
Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical
136
(
1
)
244
-
248
2007.5
-
Study on sub-THz signal input for superconducting electronic devices
Iwao Kawayama, Yasushi Doda, Ryuhei Kinjo, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi
IEICE Transactions on Electronics
E90-C
(
3
)
588
-
594
2007.3
-
Laser-terahertz emission from the chemical sensing plate
Toshihiko Kiwa, Junichi Kondo, Shohei Oka, Iwao Kawayama, Hironobu Yamada, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
2007 JOINT 32ND INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INFRARED AND MILLIMETER WAVES AND 15TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON TERAHERTZ ELECTRONICS, VOLS 1 AND 2
Vol. 1 pp. 285-286
280
-
+
2007
-
Low-frequency magnetic field detection for metal sensing
Toshihiko Kiwa, Tomoaki Kawata, Keiji Tsukada
International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics
25
(
1-4
)
447
-
451
2007
-
Hydrogen response mechanism of a proton pumping gate FET gas sensor
Keiji Tsukada, Tomiharu Yamaguchi, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironobu Yamada
Proceedings of IEEE Sensors
1326
-
1329
2007
-
Laser-terahertz emission from the chemical sensing plate
Toshihiko Kiwa, Junichi Kondo, Shohei Oka, Iwao Kawayama, Hironobu Yamada, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Keiji Tsukada
IRMMW-THz2007 - Conference Digest of the Joint 32nd International Conference on Infrared and Millimetre Waves, and 15th International Conference on Terahertz Electronics
285
-
286
2007
-
Laser-terahertz emission readout of chemical sensors
T. Kiwa, J. Kondo, S. Oka, I. Kawayama, H. Yamada, M. Tonouchi, K. Tsukada
TRANSDUCERS and EUROSENSORS '07 - 4th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems
Vol. 2, p.1915-1918, 2007
1915
-
1918
2007
-
FET型水素センサのガス選択性改善
山口富治, 滝澤正教, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2007
(
3
)
2007
-
パルス渦流探傷によるフーリエ解析手法の開発
紀和利彦, 河田知明, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2007
(
2
)
2007
-
プロトンポンピングゲート構造をもったFET型水素センサ
塚田啓二, 山口富治, 紀和利彦, 山田博信
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2007
(
3
)
2007
-
Response Properties of Proton Pumping Gate FET Hydrogen Gas Sensor
山口富治, 滝澤正教, 紀和利彦, 山口博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-07
(
23-48
)
2007
-
電解質溶液中のイオン輸送現象の磁気的解析
小林史幸, 新井裕之, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本応用磁気学会学術講演概要集
31st
2007
-
Pt-FET型水素センサの選択性評価
中田章太, 山口富治, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2007
(
3
)
2007
-
低周波磁気検査によるステンレス溶接の欠陥評価
林孝之, 林孝之, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 玉積正司, 塚田啓二
日本応用磁気学会学術講演概要集
31st
2007
-
テラヘルツ波を用いた非接触化学センサープレートの開発
紀和利彦, 近藤純一, 岡昇平, 川山巌, 山田博信, 斗内政吉, 塚田啓二
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
54th
(
3
)
2007
-
テラヘルツ波pHセンサーシステムの開発
近藤純一, 岡昇平, 紀和利彦, 山田博信, 塚田啓二, 川山巌, 斗内政吉
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2007
(
3
)
2007
-
Measurement of hydrogen gas diffusion with FET sensors
吉武剣, 坪井公輔, 山口富治, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会ケミカルセンサ研究会資料
CHS-07
(
23-48
)
2007
-
穀物水分量の新しい磁気計測方法
塚田啓二, 紀和利彦
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
54th
(
1
)
2007
-
磁場計測を用いた新しい電気化学測定システムの開発
新井裕之, 小林史幸, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会基礎・材料・共通部門大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2007
2007
-
低周波磁気検査システムを用いた積層構造内部の欠陥評価
山田博信, 石原雄大, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 玉積正司
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2007
(
1
)
2007
-
低周波磁場照射による水の磁気応答特性
塚田啓二, 増田祐生, 紀和利彦
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
54th
(
1
)
2007
-
低周波渦流探傷検査システムの金属溶接部評価への適用
長谷川照起, 石原雄大, 林孝之, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会基礎・材料・共通部門大会講演論文集(CD-ROM)
2007
2007
-
岡山大学大学院自然科学研究科 電子情報システム工学専攻 計測システム工学研究室
塚田 啓二, 紀和 利彦
電気学会論文誌. E, センサ・マイクロマシン準部門誌 = The transactions of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan. A publication of Sensors and Micromachines Society
126
(
11
)
628
-
628
2006.11
-
AC magnetic properties of large volume of water - Susceptibility measurement in unshielded environment
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa, Yuuki Masuda
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2: Letters
45
(
37-41
)
L1097
-
L1099
2006.10
-
Low-frequency eddy current imaging using mr sensor detecting tangential magnetic field components for nondestructive evaluation
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa, Tomoaki Kawata, Yudai Ishihara
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
42
(
10
)
3315
-
3317
2006.10
-
A study of fast response characteristics for hydrogen sensing with platinum FET sensor
K. Tsukada, T. Kiwa, T. Yamaguchi, S. Migitaka, Y. Goto, K. Yokosawa
Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical
114
(
1
)
158
-
163
2006.3
-
Multipoint measurements of hydrogen gas using FET type hydrogen sensors
KIWA T.
Abstract of the 11th International Meeting on Chemical Sensors (IMCS11), 2006
2006
-
Magnetic property mapping system for analyzing three-dimensional magnetic components
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa
Review of Scientific Instruments
77
(
6
)
2006
-
Hydrogen reaction characteristics of FET sensors with catalytic metal gate inhigy hydrogen concentration
K. Tsukada, T. Kiwa, T. Yamaguchi, K. Yokosawa
Proc. the 11the Int'l Meeting on Chemical Sensors (IMCS11, 16-19 July 2006)
2006
-
Humidity effect on the properties of FET-type hydrogen sensors
T. Kiwa, T. Yamaguchi, S. Nakada, K. Yokosawa, K. Tsukada
Proc. the 11the Int'l Meeting on Chemical Sensors (IMCS11, 16-19 July 2006)
2006
-
生体組織の磁気応答特性評価
宗行健太, 増田祐生, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会基礎・材料・共通部門大会(CD-ROM)
2006
2006
-
FET型水素センサによるガス濃度分布計測
吉武剣, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 横沢宏一
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2006
(
3
)
2006
-
FET型水素センサ応答特性の湿度影響評価
紀和利彦, 山口富治, 中田章太, 塚田啓二, 横沢宏一
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2006
(
3
)
2006
-
低周波磁場欠陥検査手法の開発
石原雄大, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2006
(
2
)
2006
-
低周波磁場を用いた金属欠陥の2次元マッピング
河田知明, 山田博信, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会基礎・材料・共通部門大会(CD-ROM)
2006
2006
-
Visualization of eddy current distribution and its application to nondestructive evaluation
塚田啓二, 紀和利彦, 石原雄大, 河田知明, 山田博信
日本応用磁気学会学術講演概要集
30th (CD-ROM)
2006
-
Development of NDE system using Fourier transformed eddy current method
紀和利彦, 河田知明, 山田博信, 塚田啓二
日本応用磁気学会学術講演概要集
30th (CD-ROM)
2006
-
Nondestructive evaluation of metal continuous-structure by exposing low-frequency magnetic field
山田博信, 石原雄大, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
日本応用磁気学会学術講演概要集
30th (CD-ROM)
2006
-
最近の技術から 集積回路評価用レーザーテラヘルツ放射顕微鏡の開発 ("開拓"進むテラヘルツ領域)
山下 将嗣, 紀和 利彦, 斗内 政吉
光学
34
(
9
)
472
-
474
2005.9
-
Laser terahertz emission system to investigate hydrogen gas sensors
Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada, Masato Suzuki, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Sonoko Migitaka, Koichi Yokosawa
Applied Physics Letters
86
(
26
)
1
-
3
2005.6
-
Imaging of large-scale integrated circuits using laser-terahertz emission microscopy.
International journal
Masatsugu Yamashita, Kodo Kawase, Chiko Otani, Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Optics express
13
(
1
)
115
-
20
2005.1
-
Frequency detection of focused sub-THz waves using a high-T<inf>c</inf> Josephson junction
T. Miyadera, I. Kawayama, T. Kiwa, K. Tsukada, M. Tonouchi
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
426-431
(
II
)
1726
-
1730
2005
-
Noninvasive measurements of magnetic field generated by induced current within human body under exposure to very low frequency electromagnetic fields
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2: Letters
44
(
16-19
)
L532
-
L534
2005
-
Spatial analysis of the three dimensional components of a magnetocardiogram
K. Tsukada, T. Kiwa, K. Ogata, T. Miyashita, A. Kandori
INTERMAG ASIA 2005: Digests of the IEEE International Magnetics Conference
620
-
1240
2005
-
Terahertz emission properties from palladium/silicon interface
Toshihiko Kiwa, Keiji Tsukada, Masato Suzuki, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Sonoko Migitaka, Koichi Yokosawa
Digest of Technical Papers - International Conference on Solid State Sensors and Actuators and Microsystems, TRANSDUCERS '05
1
263
-
266
2005
-
導波路結合型サブテラヘルツ電磁波発生・検出システムの開発
金城隆平, 宮寺達也, 川山巌, 村上博成, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
52nd
(
1
)
2005
-
テラヘルツ波を用いた水素センサー評価システムの構築
紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 鈴木正人, 斗内政吉, 右高園子, 横沢宏一
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
52nd
(
3
)
2005
-
空間結合型サブテラヘルツ電磁波発生・検出システムの開発
川山厳, 宮寺達也, 村上博成, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
52nd
(
1
)
2005
-
テラヘルツ電磁波による水素センサー特性評価
紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 鈴木正人, 斗内政吉, 右高園子, 横沢宏一
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2005
(
3
)
2005
-
磁気センサーを用いた金属検出器の開発
河田知明, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2005
(
2
)
2005
-
生体内誘導電流の磁気的計測方法
塚田啓二, 紀和利彦
日本ME学会大会論文集
44th
2005
-
磁気センサを用いた生体内誘導電流の計測
塚田啓二, 紀和利彦
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2005
(
2
)
2005
-
低周波磁場照射による生体内の誘導電流の磁気的計測
塚田啓二, 紀和利彦
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
52nd
(
1
)
2005
-
水素ガスセンサの感応膜の特性評価
山口富治, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 中野定樹, 右高園子, 横沢宏一
電気学会全国大会講演論文集
2005
(
3
)
2005
-
Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Detection System using Magnetic Sensors
紀和利彦, 河田知明, 塚田啓二
日本応用磁気学会学術講演概要集
29th (CD-ROM)
2005
-
THz time domain spectroscopy of pulsed laser deposited BaTiO <inf>3</inf> thin films
M. Misra, K. Kotani, T. Kiwa, I. Kawayama, H. Murakami, M. Tonouchi
Applied Surface Science
237
(
1-4
)
421
-
426
2004.10
-
Ultrafast optical study of amorphous Ge thin films for superconductor/ semiconductor hybrid devices
T. Miyadera, T. Kiwa, I. Kawayama, H. Murakami, M. Tonouchi
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
412-414
(
SPEC. ISS.
)
1602
-
1606
2004.10
-
Real-time monitoring of a photomixing signal using a high-T<inf>C</inf> Josephson junction
Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Superconductor Science and Technology
17
(
8
)
998
-
1002
2004.8
-
Terahertz radiation from InAs/Al<inf>x</inf>Ga<inf>1-x</inf>Sb (x = 0.5) heterostructures
Masato Suzuki, Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Yoji Nakajima, Shigehiko Sasa, Masataka Inoue
Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures
22
(
1-3
)
574
-
577
2004.4
-
An imaging and quantitative analysis technique for diagnosis of electro-pysiological excitation abnormality of heart
K. Tsukada, K. Ogata, T. Miyashita, S. Yamada, H. Horigome, J. Shiono, T. Kiwa, A. Kandori, I. Yamaguchi
Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Biomagnetism
2004
-
A DEVELOPMENT OF MEASURING SYSTEM OF INDUCED CURRENT IN HUMAN BODY DUE TO LOW FREQUENCY ELECTROMAGNETIC IRRADIATION
Keiji Tsukada, Toshihiko Kiwa
Proceedings of Biological Effects of EMFs, 3rd International Workshop
2004
-
LSI故障解析用レーザーテラヘルツエミッション顕微鏡の開発 レーザーテラヘルツエミッション顕微鏡による集積回路観察
山下将嗣, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, 二川清, 大谷知行, 川瀬晃道
マイクロファブリケーション研究の最新動向
15
2004
-
ジョセフソン接合を用いたフォトミキシング電磁波周波数検出・安定化システム
紀和利彦, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
51st
(
3
)
2004
-
運動負荷による心臓磁場変化の解析
塩田隆雄, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 緒方邦臣, 宮下豪, 神鳥明彦
日本ME学会秋季大会論文集
18th
2004
-
光ファイバ結合型コンパクトテラヘルツ分光ヘッドの開発
大野恭裕, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
51st
(
3
)
2004
-
光ファイバ結合型コンパクトテラヘルツ分光システムの構築
大野恭裕, 井上亮太郎, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
65th
(
3
)
2004
-
テラヘルツエミッション顕微鏡によるMOSトランジスタの非接触測定
山下将嗣, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, 二川清, 川瀬晃進
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
51st
(
3
)
2004
-
心臓磁場の空間解析
楠野順也, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 緒方邦臣, 宮下豪, 神鳥明彦
日本ME学会秋季大会論文集
18th
2004
-
レーザーテラヘルツエミッション顕微鏡による集積回路観察
山下将嗣, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, 大谷知行, 川瀬晃道
レーザ顕微鏡研究会講演会抄録集
30th
2004
-
チューナブルサブテラヘルツ電磁波発生・検出システム
宮寺達也, 川山巌, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
65th
(
1
)
2004
-
レーザーテラヘルツ放射顕微鏡
斗内政吉, 紀和利彦, 山下将嗣, 川瀬晃道
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
51st
(
0
)
2004
-
高温超伝導体におけるポンプ・プローブテラヘルツ電磁波励起観測
寺坂宏介, 富成征弘, 高橋宏平, 紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
51st
(
1
)
2004
-
心磁の3次元ベクトル成分解析
増田祐生, 紀和利彦, 塚田啓二, 緒方邦臣, 宮下豪, 神鳥明彦
日本ME学会秋季大会論文集
18th
2004
-
Generation of sub-terahertz waves using a semiconductor photomixer
Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Superconductor Science and Technology
16
(
12
)
1540
-
1543
2003.12
-
Optical response of amorphous Ge photoconductive switches with YBCO transmission lines
I. Kawayama, T. Miyadera, Y. Doda, T. Kiwa, H. Murakami, M. Tonouchi
Superconductor Science and Technology
16
(
12
)
1475
-
1478
2003.12
-
Laser terahertz-emission microscope for inspecting electrical faults in integrated circuits.
International journal
Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Masatsugu Yamashita, Kodo Kawase
Optics letters
28
(
21
)
2058
-
60
2003.11
-
Characteristics of superconducting flux flow transistors under irradiation of femtosecond laser pulses
Y. Doda, T. Kiwa, I. Kawayama, H. Murakami, M. Tonouchi
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
392-396
(
PART 2
)
1504
-
1508
2003.10
-
Terahertz Radiation from InAs/AlGaSb heterostructures
Suzuki M., Kiwa T., Tonouchi M., Nakajima Y., Sasa S., Inoue M.
Meeting abstracts of the Physical Society of Japan
58
(
2
)
657
-
657
2003.8
-
THz radiation properties of Tl<inf>2</inf>Ba<inf>2</inf>CaCu<inf>2</inf>O<inf>8+δ</inf> thin films excited by femtosecond laser pulses
Yukihiro Tominari, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Henrik Schneidewind, Hagen Wald, Paul Seidel
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
13
(
2 III
)
3730
-
3732
2003.6
-
Backscattered terahertz radiation imaging system to visualize supercurrent distributions
T. Kiwa, Y. Kamata, M. Misra, H. Murakami, M. Tonouchi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity
13
(
2 III
)
3675
-
3678
2003.6
-
Coherent terahertz radiation from Tl<inf>2</inf>Ba<inf>2</inf>CaCu<inf>2</inf>O<inf>8+δ</inf> thin films excited by optical laser pulse under magnetic field
Yukihiro Tominari, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Hagen Wald, Paul Seidel, Henrik Schneidewind
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
388-389
481
-
482
2003.5
-
THz imaging of supercurrent distribution in Meissner state of LPE-BSCCO film
H. Murakami, T. Kiwa, M. Tonouchi, T. Yasuda
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
388-389
479
-
480
2003.5
-
Photomixing Optical-Microwave Transformer Coupled with High-TC Josephson Junctions.
紀和利彦, 斗内政吉
低温工学
38
(
1
)
2003
-
後方散乱型テラヘルツ電磁波イメージングによる半導体IC断線評価
紀和利彦, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
50th
(
3
)
2003
-
Study on Optical Response of Amorphous Ge Thin Films for Superconductor-Semiconductor Hybrid Optical Interface
宮寺達也, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
103
(
367(SCE2003 19-27)
)
2003
-
Photomixer/High-TC Josephon Junction Hybrid System
紀和利彦, 鈴木正人, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
103
(
367(SCE2003 19-27)
)
2003
-
IC断線評価システムの空間分解能評価
山下将嗣, 紀和利彦, 川瀬晃道, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
64th
(
3
)
2003
-
YBa2Cu3O7-x薄膜を伝送線に持つ非晶質Ge光スイッチの低温特性
宮寺達也, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
50th
(
1
)
2003
-
非晶質Ge薄膜の高速光応答計測
宮寺達也, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 斗内政吉
光物性研究会論文集
14th
2003
-
フォトミキシング光-マイクロ波変換システム (II)
紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
64th
(
1
)
2003
-
フォトミキシング電磁波のジョセフソン接合直列アレイによる検出
紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
50th
(
1
)
2003
-
Relaxation dynamics of optically excited quasi-particles in BSCCO
H. Murakami, T. Yasuda, Y. Tominari, T. Kiwa, M. Tonouchi, T. Uchiyama, I. Iguchi, Z. Wang
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
378-381
(
PART 1
)
320
-
323
2002.10
-
Partial and macroscopic phase coherences in an underdoped Bi<inf>2</inf>Sr<inf>2</inf>CaCu<inf>2</inf>O<inf>8+δ</inf> thin film
H. Murakami, T. Kiwa, N. Kida, M. Tonouchi, T. Uchiyama, I. Iguchi, Z. Wang
Europhysics Letters
60
(
2
)
288
-
294
2002.10
-
Resonant terahertz radiation from Tl<inf>2</inf>Ba<inf>2</inf>CaCu <inf>2</inf>O<inf>8+δ</inf> thin films by ultrafast optical pulse excitation
Yukihiro Tominari, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Hagen Wald, Paul Seidel, Henrik Schneidewind
Applied Physics Letters
80
(
17
)
3147
-
3149
2002.4
-
Tetrahertz pulse radiation properties of a Bi<inf>2</inf>Sr<inf>2</inf>CaCu<inf>2</inf>O<inf>8+δ</inf> bowtie antenna by optical pulse illumination
Hironaru Murakami, Toshihiko Kiwa, Muku L. Misra, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Tetsuji Uchiyama, Ienari Iguchi, Zhen Wang
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1: Regular Papers and Short Notes and Review Papers
41
(
4
)
1992
-
1997
2002.4
-
25aYH-10 Optically excited Josephson plasma emission of THz-wave from Tl_2Ba_2CaCu_2O_<8+δ> thin films
Tominari Y., Kiwa T., Murakamic H., Tonouchi M., Wald H., Seidel P., Schneidewind H.
Meeting abstracts of the Physical Society of Japan
57
(
1
)
546
-
546
2002.3
-
24pYK-11 Ultrafast carrier dynanics in pseudgap state of BSCCO
Murakami H., Kiwa T., Tonouchi M., Uchiyama T., Iguchi I., Wang Z., Yasuda T.
Meeting abstracts of the Physical Society of Japan
57
(
1
)
506
-
506
2002.3
-
Preparation and picosecond optical response of Bi system high-T<inf>c</inf> superconductors
Yukihiro Tominari, Toshihiko Kiwa, Hironaru Murakami, Masayoshi Tonouchi, Takeshi Arai, Takafumi Aomine
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
367
(
1-4
)
332
-
336
2002.2
-
Time-domain terahertz spectroscopy of Bi<inf>2</inf>Sr<inf>2</inf>CaCu<inf>2</inf>O<inf>8+δ</inf> thin film
Hironaru Murakami, Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchil, Tetsuji Uchiyama, Ienari Iguchi, Zhen Wang
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
367
(
1-4
)
322
-
326
2002.2
-
TERAHERTZ EMISSION PROPERTIES OF JOSEPHSON JUNCTION UNDER SMALL MAGNETIC FIELD
T. Kiwa, T. Yoshimura, H. Murakami, M. Tonouchi
Singapore Journal of Phsycis
2002
-
Terahertz Radiation from Strongly Correlated Electron Systems and Related Phenomena.
斗内政吉, 貴田徳明, 紀和利彦, 富成征弘, 川山巌, 村上博成
レーザー研究
30
(
7
)
2002
-
フォトミキシング光-マイクロ波変換システム
紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
63rd
(
1
)
2002
-
フェムト秒レーザー照射によるフラックスフロートランジスタのフロー特性の変化
堂田泰史, 紀和利彦, 川山巌, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
63rd
(
1
)
2002
-
超短光パルス励起によるTl2Ba2CaCu2O8+δ薄膜からのTHz電磁波放射特性
村上博成, 富成征弘, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, WALD H, SEIDEL P, SCHNEIDEWIND H
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
49th
(
1
)
2002
-
Time-resolved pump and probe reflection spectroscopy of Y-doped BSCCO single crystal
Tominari Y., Kiwa T., Murakami H., Tonouchi M., Arai T., Aomine T., Yasuda K.
Meeting abstracts of the Physical Society of Japan
56
(
2
)
424
-
424
2001.9
-
Time-domain THz Spectroscopy of BSCCO Thin Film
Murakami H., Kiwa T., Tonouchi M., Uchiyama T., Iguchi I., Wang Z.
Meeting abstracts of the Physical Society of Japan
56
(
2
)
441
-
441
2001.9
-
High frequency properties of YBCO thin films diagnosed by time-domain terahertz spectroscopy
Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
362
(
1-4
)
314
-
318
2001.9
-
Terahertz emission from YBa<inf>2</inf>Cu<inf>3</inf>O<inf>7-δ</inf> Josephson junctions excited by femtosecond laser
Takahiro Yoshimura, Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
362
(
1-4
)
329
-
332
2001.9
-
Terahertz emission properties from YBCO thin film log-periodic antennas
Hitoshi Saijo, Masahiko Morimoto, Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications
362
(
1-4
)
319
-
323
2001.9
-
Time-domain terahertz spectroscopy of (100)(LaAlO<inf>3</inf>)<inf>0.3</inf>-(Sr<inf>2</inf> AlTaO<inf>6</inf>)<inf>0.7</inf> substrate
Toshihiko Kiwa, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2: Letters
40
(
1 A/B
)
L38
-
L40
2001.1
-
Tl2Ba2CaCu2O8+δからの光励起ジョセフソンプラズマ放射
富成征弘, 紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉, WALD H, SEIDEL P, SCHNEIDEWIND H
光物性研究会論文集
12th
2001
-
BSCCO薄膜の時間領域テラヘルツ分光
村上博成, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, 斗内政吉, 内山哲治, 内山哲治, 井口家成, 井口家成
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
48th
(
1
)
2001
-
La0.7Sr0.3MnO3-δ薄膜の作製とフェムト秒時間領域反射率変化
小谷研太, 紀和利彦, 貴田徳明, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
48th
(
1
)
2001
-
Bi2Sr2Ca0.8Y0.2CuO8+δ単結晶の作製とフェムト秒光パルス応答
富成征弘, 荒井毅, 青峰隆文, 紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
48th
(
1
)
2001
-
非晶質半導体薄膜のフェムト秒光応答とテラヘルツ電磁波放射
紀和利彦, 河崎尚寛, 吉村尚洋, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
48th
(
2
)
2001
-
Femtosecond optical response of Y dopping Bi2212 single crystal.
富成征弘, 紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉, 荒井毅, 青峰隆文
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
101
(
183(SCE2001 16-23)
)
2001
-
ポンププローブテラヘルツ電磁波励起による光励起電荷ダイナミックスの評価(II)LT-GaAsの場合
河崎尚寛, 吉村尚洋, 紀和利彦, 村上博成, 斗内政吉
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
48th
(
3
)
2001
-
Optical response in amorphous GaAs thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition
Toshihiko Kiwa, Ichiro Kawashima, Shigeki Nashima, Masanori Hangyo, Masayoshi Tonouchi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1: Regular Papers and Short Notes and Review Papers
39
(
11
)
6304
-
6308
2000.11
-
25aZF-12 Comparison of THz radiation emitted from Y_<0.7>Pr_<0.3>Ba_2Cu_3O_7 and YBa_2Cu_3O_<(7-δ)>
Wald H., Kiwa T., Nashima S., Tonouchi M., Seidel P., Hangyo M.
Meeting abstracts of the Physical Society of Japan
55
(
1
)
543
-
543
2000.3
-
時間領域テラヘルツ分光法によるYBCO薄膜の高周波物性評価
紀和利彦, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
61st
(
1
)
2000
-
アモルファス半導体薄膜からのTHz電磁波の放射特性
中山浩一, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
61st
(
3
)
2000
-
LSAT基板のテラヘルツ領域分光評価
紀和利彦, 菜嶋茂喜, 森川治, 斗内政吉, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
47th
(
1
)
2000
-
フェムト秒光パルス検出用メモリーセルの設計と作製
吉村尚洋, 森本雅彦, 西條人司, 紀和利彦, 斗内政吉, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
47th
(
1
)
2000
-
ポンププローブテラヘルツ電磁波励起によるSI-GaAs光スイッチの応答評価
吉村尚洋, 紀和利彦, WALD Hagen, 斗内政吉
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
61st
(
3
)
2000
-
Fabrication of a GaAs/YBCO layered structure and its optical response.
紀和利彦, 中山浩一, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
99
(
586(SCE99 37-44)
)
2000
-
Controllability and stability of magnetic flux in YBCO thin film loop trapped by optically induced current imbalance
Shikita, M. Yamashita, T. Kiwa, O. Morikawa, M. Tonouchi, M. Hangyo
Advances in Superconductivity XI, eds. N. Koshizuka and S. Tajima, Springer-Verlag Tokyo,
1999
-
A novel two-dimensional mapping system for supercurrent distribution using femtosecond laser pulses
T. Kondo, S. Shikii, M. Yamashita, T. Kiwa, O. Morikawa, M. Tonouchi, M. Hangyo, M. Tani, K. Sakai
Advances in Superconductivity XI, eds. N. Koshizuka and S. Tajima, Springer-Verlag Tokyo,
1999
-
Evaluation of the supercurrent distribution by terahertz radiation mapping
M. Yamashita, S. Shikii, T. Kondo, T. Kiwa, M. Tonouchi, M. Hangyo
Advances in Superconductivity XI, eds. N. Koshizuka and S. Tajima, Springer-Verlag Tokyo,
1999
-
YBa2Cu3O7-δ上へのアモルファスGaAs成長と光応答評価
紀和利彦, 菜嶋茂喜, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
46th
(
1
)
1999
-
Magnetic flux generation in YBCO thin film loops by optical excitation under magnetic field.
西条人司, 山下将嗣, 紀和利彦, 近藤孝志, 森川治, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
59th
(
1
)
1998
-
Magnetic flux trap in ion implanted YBCO thin films diagnosed by terahertz mapping.
紀和利彦, 山下将嗣, 森川治, 中村孝夫, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
59th
(
1
)
1998
-
Effect of Magnetic Lenz on Magnetocardiogram Measurement.
中道真也, 紀和利彦, 藤井龍彦, 神代万亀夫, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学関係連合講演会講演予稿集
45th
(
1
)
1998
-
Control and visualization of magnetic flux quanta in high-Tc superconductive loops.
斗内政吉, 鋪田和夫, 紀和利彦, 山下将嗣, 森川治, 萩行正憲
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
59th
(
1
)
1998
-
The effect of the magnetic flux trap in YBCO thin films for supercurrent distribution THz mapping.
山下将嗣, 近藤孝志, 紀和利彦, 森川治, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
59th
(
1
)
1998
-
Controllability and stability of magnetic flux trapped in YBCO thin film loop with femtosecond laser pulses.
鋪田和夫, 山下将嗣, 紀和利彦, 森川治, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲
応用物理学会学術講演会講演予稿集
59th
(
1
)
1998
-
Visualization of Supercurrent Distribution in YBCO Thin Films.
山下将嗣, 近藤孝志, 紀和利彦, 森川治, 斗内政吉, 萩行正憲, 谷正彦, 阪井清美
電子情報通信学会技術研究報告
98
(
342(LQE98 73-87)
)
1998